Actions required to implement integrated care for older people in the community using the World Health Organization's ICOPE approach: A global Delphi consensus study
- PMID: 30308077
- PMCID: PMC6181385
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0205533
Actions required to implement integrated care for older people in the community using the World Health Organization's ICOPE approach: A global Delphi consensus study
Abstract
Background: Integrated care is recognised as an important enabler to healthy ageing, yet few countries have managed to sustainably deliver integrated care for older people. We aimed to gather global consensus on the key actions required to realign health and long-term systems and integrate services to implement the World Health Organization (WHO) Integrated Care for Older People (ICOPE) approach.
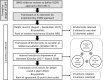
Methods: A two-round eDelphi study, including a global consultation meeting, was undertaken to identify, refine and generate consensus on the actions required across high-, middle- and low-income countries to implement the WHO ICOPE approach. In round 1, a framework of 31 actions, empirically derived from previous WHO evidence reviews was presented to panellists to judge the relative importance of each action (numeric rating scale; range:1-9) and provide free-text comments concerning the scope of the actions. These outcomes were discussed and debated at the global consultation meeting. In round 2, a revised framework of 19 actions was presented to panellists to measure their extent of agreement and identify 'essential' actions (five-point Likert scale; range: strongly agree to strongly disagree). A threshold of ≥80% for agree/strongly agree was set a priori for consensus.
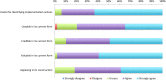
Results: After round 1 (n = 80 panellists), median scores across 31 actions ranged from 6 to 9. Based on pre-defined category thresholds for median scores, panellists considered 28 actions (90·3%) as 'important' and three (9·7%) as 'uncertain'. Fifteen additional actions were suggested for inclusion based on free-text comments, creating 46 for consideration at the global consultation meeting. In round 2 (n = 84 panellists), agreement (agree or strongly agree) ranged from 84·6-97·6%, suggesting consensus. Fourteen (73·7%) actions were rated as essential.
Conclusion: Fourteen essential actions and five important actions are necessary at system (macro; n = 10) and service (meso; n = 9) levels to implement community-based integrated care for older people.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
International research priorities for integrated care and cross-boundary working: an electronic Delphi study.Int J Qual Health Care. 2024 Oct 14;36(4):mzae095. doi: 10.1093/intqhc/mzae095. Int J Qual Health Care. 2024. PMID: 39330981 Free PMC article.
-
Consensus on pre-operative total knee replacement education and prehabilitation recommendations: a UK-based modified Delphi study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021 Apr 14;22(1):352. doi: 10.1186/s12891-021-04160-5. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021. PMID: 33853564 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the Readiness for Implementing the World Health Organization's ICOPE Approach in Hong Kong: Perspectives from Social Care and Policy Stakeholders.J Frailty Aging. 2023;12(2):126-133. doi: 10.14283/jfa.2023.3. J Frailty Aging. 2023. PMID: 36946709
-
What outcomes should be measured in feline chronic kidney disease treatment trials? Establishing a core outcome set for research.Prev Vet Med. 2021 Jul;192:105348. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2021.105348. Epub 2021 Apr 16. Prev Vet Med. 2021. PMID: 34022713
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
System strengthening to support value-based care and healthy ageing for people with chronic pain.Pain. 2019 Jun;160(6):1240-1244. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001526. Pain. 2019. PMID: 30908354 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Health system strengthening is needed to respond to the burden of pain in low- and middle-income countries and to support healthy ageing.J Glob Health. 2019 Dec;9(2):020317. doi: 10.7189/jogh.09.020317. J Glob Health. 2019. PMID: 33274068 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Integrated Care Services for Dementia and Their Challenges from a Nursing Home Perspective: An Ethnographic Study.Int J Integr Care. 2024 Dec 13;24(4):12. doi: 10.5334/ijic.8592. eCollection 2024 Oct-Dec. Int J Integr Care. 2024. PMID: 39677920 Free PMC article.
-
The World Health Organization (WHO) Integrated Care for Older People (ICOPE) Framework: A Narrative Review on Its Adoption Worldwide and Lessons Learnt.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Dec 22;20(1):154. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20010154. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36612480 Free PMC article.
-
Perceptions and Expectations of Advanced Geriatric Nursing Role Development in Primary Health Care: A Qualitative Study Exploring Staff's Perspectives.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2021 Dec 30;14:3607-3619. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S343622. eCollection 2021. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2021. PMID: 35002250 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organisation. World Report on Ageing and Health Geneva: WHO, 2015.
-
- World Health Organisation. Global strategy and action plan on ageing and health Geneva: World Health Organization, 2016.
-
- World Health Organization. Framework on integrated, people-centred health services Geneva: World Health Organization, 2016. Contract No.: A69/39.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources