Hydrophobic Amino Acid Tryptophan Shows Promise as a Potential Absorption Enhancer for Oral Delivery of Biopharmaceuticals
- PMID: 30308982
- PMCID: PMC6321321
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics10040182
Hydrophobic Amino Acid Tryptophan Shows Promise as a Potential Absorption Enhancer for Oral Delivery of Biopharmaceuticals
Abstract
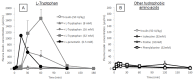
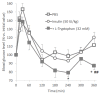
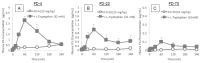
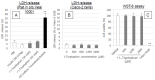
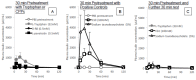
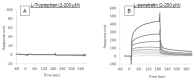
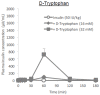
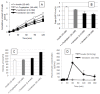
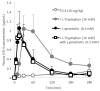
Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) have great potential to efficiently deliver drug cargos across cell membranes without cytotoxicity. Cationic arginine and hydrophobic tryptophan have been reported to be key component amino acids for cellular internalization of CPPs. We recently found that l-arginine could increase the oral delivery of insulin in its single amino acid form. Therefore, in the present study, we evaluated the ability of another key amino acid, tryptophan, to enhance the intestinal absorption of biopharmaceuticals. We demonstrated that co-administration with l-tryptophan significantly facilitated the oral and intestinal absorption of the peptide drug insulin administered to rats. Furthermore, l-tryptophan exhibited the ability to greatly enhance the intestinal absorption of other peptide drugs such as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), its analog Exendin-4 and macromolecular hydrophilic dextrans with molecular weights ranging from 4000 to 70,000 g/mol. However, no intermolecular interaction between insulin and l-tryptophan was observed and no toxic alterations to epithelial cellular integrity-such as changes to cell membranes, cell viability, or paracellular tight junctions-were found. This suggests that yet to be discovered inherent biological mechanisms are involved in the stimulation of insulin absorption by co-administration with l-tryptophan. These results are the first to demonstrate the significant potential of using the single amino acid l-tryptophan as an effective and versatile bioavailability enhancer for the oral delivery of biopharmaceuticals.
Keywords: GLP-1; amino acid; cell-penetrating peptide; insulin; intestinal absorption; oral delivery; tryptophan.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



References
-
- Salzano G., Torchilin V.P. Intracellular delivery of nanoparticles with cell penetrating peptides. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015;1324:357–368. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

