Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling as a Potential Target for the Treatment of Liver Cirrhosis Using Antifibrotic Drugs
- PMID: 30308992
- PMCID: PMC6213128
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19103103
Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling as a Potential Target for the Treatment of Liver Cirrhosis Using Antifibrotic Drugs
Abstract
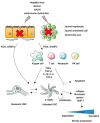
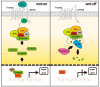
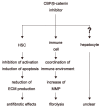
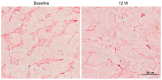
Cirrhosis is a form of liver fibrosis resulting from chronic hepatitis and caused by various liver diseases, including viral hepatitis, alcoholic liver damage, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, and autoimmune liver disease. Cirrhosis leads to various complications, resulting in poor prognoses; therefore, it is important to develop novel antifibrotic therapies to counter liver cirrhosis. Wnt/β-catenin signaling is associated with the development of tissue fibrosis, making it a major therapeutic target for treating liver fibrosis. In this review, we present recent insights into the correlation between Wnt/β-catenin signaling and liver fibrosis and discuss the antifibrotic effects of the cAMP-response element binding protein/β-catenin inhibitor PRI-724.
Keywords: PRI-724; Wnt; liver fibrosis; β-catenin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

