Tim-3 expression and its role in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 30309387
- PMCID: PMC6182863
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-018-0667-4
Tim-3 expression and its role in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
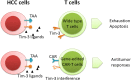
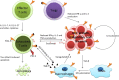
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common tumors in the world, and its mortality is still on the rise. Limited treatments and low chemotherapy sensitivity of HCC make new therapeutic strategies urgently needed. With the rise of immune checkpoint blockade, anti-CTLA-4 antibodies and anti-PD-1 antibodies have shown therapeutic effects in various tumors. T cell immunoglobulin mucin-3 (Tim-3), a newly discovered immune checkpoint molecule, plays a major role in the development of HCC. Tim-3 can be used to evaluate the prognosis and therapeutic effects in HCC, and Tim-3 intervention has shown anti-tumor effects in preclinical experiments. This review summarizes findings regarding Tim-3 and HCC in recent years and discusses the rationale of Tim-3 as a therapeutic target for HCC.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Immune checkpoint blockade; Immunotherapy; Tim-3.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immune checkpoint proteins PD-1 and TIM-3 are both highly expressed in liver tissues and correlate with their gene polymorphisms in patients with HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Dec;95(52):e5749. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005749. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 28033288 Free PMC article.
-
Repression of lncRNA NEAT1 enhances the antitumor activity of CD8+T cells against hepatocellular carcinoma via regulating miR-155/Tim-3.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019 May;110:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2019.01.019. Epub 2019 Jan 30. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 30710754
-
Blocking Tim-3 or/and PD-1 reverses dysfunction of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma.Bull Cancer. 2018 May;105(5):493-501. doi: 10.1016/j.bulcan.2018.01.018. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Bull Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29576222
-
Role of Tim-3 in hepatitis B virus infection: An overview.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Feb 21;22(7):2294-303. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i7.2294. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 26900291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of TIM-3 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Promising Target for Immunotherapy?Front Oncol. 2020 Dec 3;10:601661. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.601661. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33425759 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unveiling the tumor immune microenvironment of organ-specific melanoma metastatic sites.J Immunother Cancer. 2022 Sep;10(9):e004884. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-004884. J Immunother Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36096531 Free PMC article.
-
Immunotherapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Current Limits and Prospects.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 29;11:589680. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.589680. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33854960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunomodulatory effects of regorafenib: Enhancing the efficacy of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 2;13:992611. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.992611. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36119072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PD1 and TIM3 Expression is Associated with Very Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence After Percutaneous Thermal Ablation.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024 Jan 9;11:39-50. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S443134. eCollection 2024. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024. PMID: 38223553 Free PMC article.
-
Red Blood Cell-Mimic Nanocatalyst Triggering Radical Storm to Augment Cancer Immunotherapy.Nanomicro Lett. 2022 Feb 5;14(1):57. doi: 10.1007/s40820-022-00801-z. Nanomicro Lett. 2022. PMID: 35122163 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Binnewies M, Roberts EW, Kersten K, Chan V, Fearon DF, Merad M, Coussens LM, Gabrilovich DI, Ostrand-Rosenberg S, Hedrick CC, Vonderheide RH, Pittet MJ, Jain RK, Zou W, Howcroft TK, Woodhouse EC, Weinberg RA, Krummel MF. Understanding the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) for effective therapy. Nat Med. 2018;24(5):541–550. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0014-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

