Stress Cardiomyopathy Diagnosis and Treatment: JACC State-of-the-Art Review
- PMID: 30309474
- PMCID: PMC7058348
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.07.072
Stress Cardiomyopathy Diagnosis and Treatment: JACC State-of-the-Art Review
Abstract
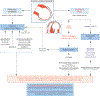
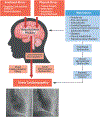
Stress cardiomyopathy is an acute reversible heart failure syndrome initially believed to represent a benign condition due to its self-limiting clinical course, but now recognized to be associated with a non-negligible rate of serious complications such as ventricular arrhythmias, systemic thromboembolism, and cardiogenic shock. Due to an increased awareness and recognition, the incidence of stress cardiomyopathy has been rising (15-30 cases per 100,000 per year), although the true incidence is unknown as the condition is likely underdiagnosed. Stress cardiomyopathy represents a form of neurocardiogenic myocardial stunning, and while the link between the brain and the heart is established, the exact pathophysiological mechanisms remain unclear. We herein review the proposed risk factors and triggers for the syndrome and discuss a practical approach to diagnosis and treatment of the patients with stress cardiomyopathy, highlighting potential challenges and unresolved questions.
Keywords: Takotsubo; cardiomyopathy; stress.
Copyright © 2018 American College of Cardiology Foundation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Sato H, Tateishi H, Dote K, et al. Tako-tsubo like left ventricular dysfunction due to multivessel coronary spasm In: Kodama K, Haze K, Hori M, editors. Clinical Aspects of Myocardial Injury: From Ischemia to Heart Failure. Tokyo: Tokio Kagakuhyoronsha Publ Co., 1990:56–64.
-
- Hurst RT, Prasad A, Askew JW, Sengupta PP, Tajik AJ. Takotsubo cardiomyopathy: a unique cardiomyopathy with variable ventricular morphology. J Am Coll Cardiol Img 2010;3:641–9. - PubMed
-
- Medeiros K, O’Connor MJ, Baicu CF, et al. Systolic and diastolic mechanics in stress cardiomyopathy. Circulation 2014;129:1659–67. - PubMed
-
- Kurisu S, Sato H, Kawagoe T, et al. Tako-tsubo-like left ventricular dysfunction with ST-segment elevation: a novel cardiac syndrome mimicking acute myocardial infarction. Am Heart J 2002;143: 448–55. - PubMed
-
- Gianni M, Dentali F, Grandi AM, Sumner G, Hiralal R, Lonn E. Apical ballooning syndrome or takotsubo cardiomyopathy: a systematic review. Eur Heart J 2006;27:1523–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

