Clinical effectiveness of the Manchester Glaucoma Enhanced Referral Scheme
- PMID: 30309913
- PMCID: PMC6678050
- DOI: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2018-312385
Clinical effectiveness of the Manchester Glaucoma Enhanced Referral Scheme
Abstract
Background: Glaucoma referral filtering schemes have operated in the UK for many years. However, there is a paucity of data on the false-negative (FN) rate. This study evaluated the clinical effectiveness of the Manchester Glaucoma Enhanced Referral Scheme (GERS), estimating both the false-positive (FP) and FN rates.
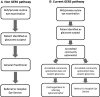
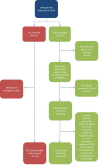
Method: Outcome data were collected for patients newly referred through GERS and assessed in 'usual-care' clinics to determine the FP rate (referred patients subsequently discharged at their first visit). For the FN rate, glaucoma suspects deemed not requiring referral following GERS assessment were invited to attend for a 'reference standard' examination including all elements of assessment recommended by National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) by a glaucoma specialist optometrist. A separate 33 cases comprising randomly selected referred and non-referred cases were reviewed independently by two glaucoma specialist consultant ophthalmologists to validate the reference standard assessment.
Results: 1404 patients were evaluated in GERS during the study period; 651 (46.3%) were referred to the Hospital Eye Service (HES) and 753 (53.6%) were discharged. The FP rate in 307 assessable patients referred to the HES was 15.5%. This study reviewed 131 (17.4%) of those patients not referred to the HES through the GERS scheme; 117 (89.3%) were confirmed as not requiring hospital follow-up; 14 (10.7%) required follow-up, including 5 (3.8%) offered treatment. Only one patient (0.8%) in this sample met the GERS referral criteria and was not referred (true FN). There were no cases of missed glaucoma or non-glaucomatous pathology identified within our sample.
Conclusion: The Manchester GERS is an effective glaucoma filtering scheme with a low FP and FN rate.
Keywords: glaucoma.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2019. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Ratnarajan G, Newsom W, Vernon SA, et al. . The effectiveness of schemes that refine referrals between primary and secondary care—the UK experience with glaucoma referrals: the Health Innovation & Education Cluster (HIEC) Glaucoma Pathways Project. BMJ Open 2013;3:e002715 10.1136/bmjopen-2013-002715 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
