Using deep autoencoders to identify abnormal brain structural patterns in neuropsychiatric disorders: A large-scale multi-sample study
- PMID: 30311316
- PMCID: PMC6492107
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.24423
Using deep autoencoders to identify abnormal brain structural patterns in neuropsychiatric disorders: A large-scale multi-sample study
Abstract
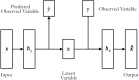
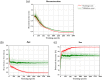
Machine learning is becoming an increasingly popular approach for investigating spatially distributed and subtle neuroanatomical alterations in brain-based disorders. However, some machine learning models have been criticized for requiring a large number of cases in each experimental group, and for resembling a "black box" that provides little or no insight into the nature of the data. In this article, we propose an alternative conceptual and practical approach for investigating brain-based disorders which aim to overcome these limitations. We used an artificial neural network known as "deep autoencoder" to create a normative model using structural magnetic resonance imaging data from 1,113 healthy people. We then used this model to estimate total and regional neuroanatomical deviation in individual patients with schizophrenia and autism spectrum disorder using two independent data sets (n = 263). We report that the model was able to generate different values of total neuroanatomical deviation for each disease under investigation relative to their control group (p < .005). Furthermore, the model revealed distinct patterns of neuroanatomical deviations for the two diseases, consistent with the existing neuroimaging literature. We conclude that the deep autoencoder provides a flexible and promising framework for assessing total and regional neuroanatomical deviations in neuropsychiatric populations.
Keywords: autism spectrum disorder; computational psychiatry; deep autoencoder; deep learning; schizophrenia; structural MRI.
© 2018 The Authors. Human Brain Mapping published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Abadi M, Agarwal A, Barham P, Brevdo E, Chen Z, Citro C, Corrado GS, Davis A, Dean J, Devin M (2016). Tensorflow: Large‐scale machine learning on heterogeneous distributed systems. arXiv Preprint, arXiv160304467.
-
- Abou‐Saleh, M. T. (2006). Neuroimaging in psychiatry: An update. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 61, 289–293. - PubMed
-
- Bhalla, M. , & Mahmood, H. (2015). Assessing accuracy of automated segmentation methods for brain lateral ventricles in MRI data. Queen's Science Undergraduate Research Journal, 1, 25–30.
-
- Cauda, F. , Geda, E. , Sacco, K. , D'agata, F. , Duca, S. , Geminiani, G. , & Keller, R. (2011). Grey matter abnormality in autism spectrum disorder: An activation likelihood estimation meta‐analysis study. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 82, 1304–1313. - PubMed
-
- Cheung B, Livezey JA, Bansal AK, Olshausen BA (2014): Discovering hidden factors of variation in deep networks. arXiv.1412.6583: 1–10.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 MH097435/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- Wellcome Trust, Grant/Award: 208519/Z/17/Z; Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo, Grant/Award Number: 2013/05168-7; Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo, Grant/Award Number: 2013/10498-6; Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior/International
- U54 MH091657/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH084803/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

