Dlk1-Dio3 locus-derived lncRNAs perpetuate postmitotic motor neuron cell fate and subtype identity
- PMID: 30311912
- PMCID: PMC6221546
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.38080
Dlk1-Dio3 locus-derived lncRNAs perpetuate postmitotic motor neuron cell fate and subtype identity
Erratum in
-
Correction: Dlk1-Dio3 locus-derived LncRNAs perpetuate postmitotic motor neuron cell fate and subtype identity.Elife. 2020 Feb 5;9:e55647. doi: 10.7554/eLife.55647. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32020893 Free PMC article.
Abstract
The mammalian imprinted Dlk1-Dio3 locus produces multiple long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) from the maternally inherited allele, including Meg3 (i.e., Gtl2) in the mammalian genome. Although this locus has well-characterized functions in stem cell and tumor contexts, its role during neural development is unknown. By profiling cell types at each stage of embryonic stem cell-derived motor neurons (ESC~MNs) that recapitulate spinal cord development, we uncovered that lncRNAs expressed from the Dlk1-Dio3 locus are predominantly and gradually enriched in rostral motor neurons (MNs). Mechanistically, Meg3 and other Dlk1-Dio3 locus-derived lncRNAs facilitate Ezh2/Jarid2 interactions. Loss of these lncRNAs compromises the H3K27me3 landscape, leading to aberrant expression of progenitor and caudal Hox genes in postmitotic MNs. Our data thus illustrate that these lncRNAs in the Dlk1-Dio3 locus, particularly Meg3, play a critical role in maintaining postmitotic MN cell fate by repressing progenitor genes and they shape MN subtype identity by regulating Hox genes.
Keywords: Ezh2; H3K27me3; Hox; Meg3; developmental biology; long noncoding RNA (lncRNA); motor neuron; mouse; neuroscience.
Plain language summary
When a gene is active, its DNA sequence is ‘transcribed’ to form a molecule of RNA. Many of these RNAs act as templates for making proteins. But for some genes, the protein molecules are not their final destinations. Their RNA molecules instead help to control gene activity, which can alter the behaviour or the identity of a cell. For example, experiments performed in individual cells suggest that so-called long non-coding RNAs (or lncRNAs for short) guide how stem cells develop into different types of mature cells. However, it is not clear whether lncRNAs play the same critical role in embryos.Yen et al. used embryonic stem cells to model how motor neurons develop in the spinal cord of mouse embryos. This revealed that motor neurons produce large amounts of a specific group of lncRNAs, particularly one called Meg3. Further experiments showed that motor neurons in mouse embryos that lack Meg3 do not correctly silence a set of genes called the Hox genes, which are crucial for laying out the body plans of many different animal embryos. These neurons also incorrectly continue to express genes that are normally active in an early phase of the stem-like cells that make motor neurons.There is wide interest in how lncRNAs help to regulate embryonic development. With this new knowledge of how Meg3 regulates the activity of Hox genes in motor neurons, research could now be directed toward investigating whether lncRNAs help other tissues to develop in a similar way.
© 2018, Yen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
YY, WH, YT, YL, EL, HH, YC, TL, MC, JL, SL, JH, JC No competing interests declared
Figures





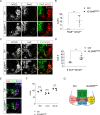
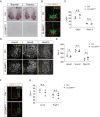
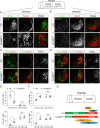


Similar articles
-
Loss of non-coding RNA expression from the DLK1-DIO3 imprinted locus correlates with reduced neural differentiation potential in human embryonic stem cell lines.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015 Jan 5;6(1):1. doi: 10.1186/scrt535. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 25559585 Free PMC article.
-
At least ten genes define the imprinted Dlk1-Dio3 cluster on mouse chromosome 12qF1.PLoS One. 2009;4(2):e4352. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004352. Epub 2009 Feb 5. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19194500 Free PMC article.
-
Meg3 Non-coding RNA Expression Controls Imprinting by Preventing Transcriptional Upregulation in cis.Cell Rep. 2018 Apr 10;23(2):337-348. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.03.044. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 29641995
-
[Review on the genomic imprinting at the mammalian DLK1-DIO3 cluster.].Yi Chuan. 2010 Aug;32(8):769-78. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1005.2010.00769. Yi Chuan. 2010. PMID: 20709673 Review. Chinese.
-
The microRNAs within the DLK1-DIO3 genomic region: involvement in disease pathogenesis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Mar;70(5):795-814. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1080-8. Epub 2012 Jul 24. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 22825660 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs mediate precise control of spinal interneuron populations to exert delicate sensory-to-motor outputs.Elife. 2021 Mar 31;10:e63768. doi: 10.7554/eLife.63768. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33787491 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of CRTC1 Is Involved in CUMS-Induced Depression-Like Behavior in the Hippocampus and Its RNA Sequencing Analysis.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Jul;59(7):4405-4418. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02787-6. Epub 2022 May 13. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35556215
-
Urine Sample-Derived Cerebral Organoids Suitable for Studying Neurodevelopment and Pharmacological Responses.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 May 14;8:304. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00304. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32528947 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal expression profiles of lncRNA and mRNA in human embryonic stem cell-derived motor neurons during differentiation.PeerJ. 2020 Nov 13;8:e10075. doi: 10.7717/peerj.10075. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 33240592 Free PMC article.
-
Long Noncoding RNAs-Crucial Players Organizing the Landscape of the Neuronal Nucleus.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 27;22(7):3478. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073478. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33801737 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 104 - 2321-B-002 - 043/Ministry of Science and Technology/International
- 104 - 2311-B-009 - 002-MY3/Ministry of Science and Technology/International
- 105 - 2221-E-009 - 126-MY3/Ministry of Science and Technology/International
- NHRI-EX106-10315N/National Health Research Institutes/International
- 104-2311-B-001 -030 -MY3/Ministry of Science and Technology/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

