The Forgotten Lipids: Triglycerides, Remnant Cholesterol, and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Risk
- PMID: 30312399
- PMCID: PMC6416708
- DOI: 10.1210/er.2018-00184
The Forgotten Lipids: Triglycerides, Remnant Cholesterol, and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Risk
Abstract
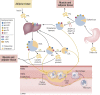
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) remains the leading cause of death worldwide. Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) is a well-established mediator of atherosclerosis and a key target for intervention for the primary and secondary prevention of ASCVD. However, despite substantial reduction in LDL-C, patients continue to have recurrent ASCVD events. Hypertriglyceridemia may be an important contributor of this residual risk. Observational and genetic epidemiological data strongly support a causal role of triglycerides (TGs) and the cholesterol content within triglyceride-rich lipoproteins (TGRLs) and/or remnant cholesterol (RC) in the development of ASCVD. TGRLs are composed of hepatically derived very low-density lipoprotein and intestinally derived chylomicrons. RC is the cholesterol content of all TGRLs and plasma TGs serve as a surrogate measure of TGRLs and RC. Although lifestyle modification remains the cornerstone for management of hypertriglyceridemia, many novel drugs are in development and have shown impressive efficacy in lowering TG levels. Several ongoing, randomized controlled trials are underway to examine the impact of these novel agents on ASCVD outcomes. In this comprehensive review, we provide an overview of the biology, epidemiology, and genetics of TGs and ASCVD; we discuss current and novel TG-lowering therapies under development.
Copyright © 2019 Endocrine Society.
Figures
References
-
- Stone NJ, Robinson JG, Lichtenstein AH, Bairey Merz CN, Blum CB, Eckel RH, Goldberg AC, Gordon D, Levy D, Lloyd-Jones DM, McBride P, Schwartz JS, Shero ST, Smith SC Jr, Watson K, Wilson PW; American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines . 2013 ACC/AHA guideline on the treatment of blood cholesterol to reduce atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines [published correction appears in J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63(25 Pt B):3024–3025] J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63(25 Pt B)2889–2934. - PubMed
-
- Catapano AL, Graham I, De Backer G, Wiklund O, Chapman MJ, Drexel H, Hoes AW, Jennings CS, Landmesser U, Pedersen TR, Reiner Ž, Riccardi G, Taskinen MR, Tokgozoglu L, Verschuren WMM, Vlachopoulos C, Wood DA, Zamorano JL, Cooney MT; ESC Scientific Document Group . 2016 ESC/EAS guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias. Eur Heart J. 2016;37(39):2999–3058. - PubMed
-
- Jacobson TA, Ito MK, Maki KC, Orringer CE, Bays HE, Jones PH, McKenney JM, Grundy SM, Gill EA, Wild RA, Wilson DP, Brown WV. National Lipid Association recommendations for patient-centered management of dyslipidemia: part 1--full report. J Clin Lipidol. 2015;9(2):129–169. - PubMed
-
- Ference BA, Yoo W, Alesh I, Mahajan N, Mirowska KK, Mewada A, Kahn J, Afonso L, Williams KA Sr, Flack JM. Effect of long-term exposure to lower low-density lipoprotein cholesterol beginning early in life on the risk of coronary heart disease: a Mendelian randomization analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60(25):2631–2639. - PubMed
-
- Cohen JC, Boerwinkle E, Mosley TH Jr, Hobbs HH. Sequence variations in PCSK9, low LDL, and protection against coronary heart disease. N Engl J Med. 2006;354(12):1264–1272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

