Genomic coordinates and continental distribution of 120 blood group variants reported by the 1000 Genomes Project
- PMID: 30312480
- PMCID: PMC7302860
- DOI: 10.1111/trf.14953
Genomic coordinates and continental distribution of 120 blood group variants reported by the 1000 Genomes Project
Abstract
Background: The 1000 Genomes Project provides a database of genomic variants from whole genome sequencing of 2504 individuals across five continental superpopulations. This database can enrich our background knowledge of worldwide blood group variant geographic distribution and identify novel variants of potential clinical significance.
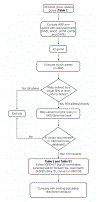
Study design and methods: The 1000 Genomes database was analyzed to 1) expand knowledge about continental distributions of known blood group variants, 2) identify novel variants with antigenic potential and their geographic association, and 3) establish a baseline scaffold of chromosomal coordinates to translate next-generation sequencing output files into a predicted red blood cell (RBC) phenotype.
Results: Forty-two genes were investigated. A total of 604 known variants were mapped to the GRCh37 assembly; 120 of these were reported by 1000 Genomes in at least one superpopulation. All queried variants, including the ACKR1 promoter silencing mutation, are located within exon pull-down boundaries. The analysis yielded 41 novel population distributions for 34 known variants, as well as 12 novel blood group variants that warrant further validation and study. Four prediction algorithms collectively flagged 79 of 109 (72%) known antigenic or enzymatically detrimental blood group variants, while 4 of 12 variants that do not result in an altered RBC phenotype were flagged as deleterious.
Conclusion: Next-generation sequencing has known potential for high-throughput and extended RBC phenotype prediction; a database of GRCh37 and GRCh38 chromosomal coordinates for 120 worldwide blood group variants is provided as a basis for this clinical application.
© 2018 AABB.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare having no competing financial interest relevant to this article.
Figures

References
-
- Sudmant PH, Rausch T, Gardner EJ, Handsaker RE, Abyzov A, Huddleston J, Zhang Y, Ye K, Jun G, Fritz MH, Konkel MK, Malhotra A, Stutz AM, Shi X, Casale FP, Chen J, Hormozdiari F, Dayama G, Chen K, Malig M, Chaisson MJP, Walter K, Meiers S, Kashin S, Garrison E, Auton A, Lam HYK, Mu XJ, Alkan C, Antaki D, Bae T, Cerveira E, Chines P, Chong Z, Clarke L, Dal E, Ding L, Emery S, Fan X, Gujral M, Kahveci F, Kidd JM, Kong Y, Lameijer EW, McCarthy S, Flicek P, Gibbs RA, Marth G, Mason CE, Menelaou A, Muzny DM, Nelson BJ, Noor A, Parrish NF, Pendleton M, Quitadamo A, Raeder B, Schadt EE, Romanovitch M, Schlattl A, Sebra R, Shabalin AA, Untergasser A, Walker JA, Wang M, Yu F, Zhang C, Zhang J, Zheng-Bradley X, Zhou W, Zichner T, Sebat J, Batzer MA, McCarroll SA, Genomes Project C, Mills RE, Gerstein MB, Bashir A, Stegle O, Devine SE, Lee C, Eichler EE, Korbel JO. An integrated map of structural variation in 2,504 human genomes. Nature 2015;526: 75–81. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Green ED, Guyer MS, National Human Genome Research I. Charting a course for genomic medicine from base pairs to bedside. Nature 2011;470: 204–13. - PubMed
-
- Kalia SS, Adelman K, Bale SJ, Chung WK, Eng C, Evans JP, Herman GE, Hufnagel SB, Klein TE, Korf BR, McKelvey KD, Ormond KE, Richards CS, Vlangos CN, Watson M, Martin CL, Miller DT. Recommendations for reporting of secondary findings in clinical exome and genome sequencing, 2016 update (ACMG SF v2.0): a policy statement of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics. Genet Med 2017;19: 249–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

