Role of inflammatory signaling in atrial fibrillation
- PMID: 30316645
- PMCID: PMC6447485
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2018.10.020
Role of inflammatory signaling in atrial fibrillation
Abstract
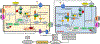
Atrial fibrillation (AF), the most prevalent arrhythmia, is often associated with enhanced inflammatory response. Emerging evidence points to a causal role of inflammatory signaling pathways in the evolution of atrial electrical, calcium handling and structural remodeling, which create the substrate of AF development. In this review, we discuss the clinical evidence supporting the association between inflammatory indices and AF development, the molecular and cellular mechanisms of AF, which appear to involve multiple canonical inflammatory pathways, and the potential of anti-inflammatory therapeutic approaches in AF prevention/treatment.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; IL-1β; Inflammasome; Inflammation; NFκB; TNF-α.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Feigin VL, Norrving B, Mensah GA. Global Burden of Stroke. Circ Res. 120 (2017) 439–448. - PubMed
-
- Iwasaki YK, Nishida K, Kato T, Nattel S. Atrial fibrillation pathophysiology: implications for management. Circulation. 124 (2011) 2264–2274. - PubMed
-
- Andrade J, Khairy P, Dobrev D, Nattel S. The clinical profile and pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation: relationships among clinical features, epidemiology, and mechanisms. Circ Res. 114, (2014) 1453–1468. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

