Activation of oxytocin neurons in the paraventricular nucleus drives cardiac sympathetic nerve activation following myocardial infarction in rats
- PMID: 30320228
- PMCID: PMC6172223
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-018-0169-5
Activation of oxytocin neurons in the paraventricular nucleus drives cardiac sympathetic nerve activation following myocardial infarction in rats
Abstract
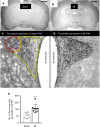
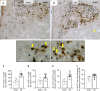
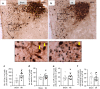
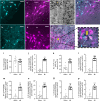
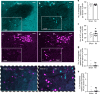
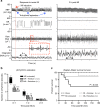
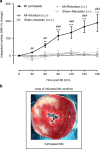
Myocardial infarction (MI) initiates an increase in cardiac sympathetic nerve activity (SNA) that facilitates potentially fatal arrhythmias. The mechanism(s) underpinning sympathetic activation remain unclear. Some neuronal populations within the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN) have been implicated in SNA. This study elucidated the role of the PVN in triggering cardiac SNA following MI (left anterior descending coronary artery ligation). By means of c-Fos, oxytocin, and vasopressin immunohistochemistry accompanied by retrograde tracing we showed that MI activates parvocellular oxytocin neurons projecting to the rostral ventral lateral medulla. Central inhibition of oxytocin receptors using atosiban (4.5 µg in 5 µl, i.c.v.), or retosiban (3 mg/kg, i.v.), prevented the MI-induced increase in SNA and reduced the incidence of ventricular arrhythmias and mortality. In conclusion, pre-autonomic oxytocin neurons can drive the increase in cardiac SNA following MI and peripheral administration of an oxytocin receptor blocker could be a plausible therapeutic strategy to improve outcomes for MI patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acute myocardial infarction activates magnocellular vasopressin and oxytocin neurones.J Neuroendocrinol. 2019 Dec;31(12):e12808. doi: 10.1111/jne.12808. J Neuroendocrinol. 2019. PMID: 31715034
-
Delayed coronary reperfusion is ineffective at impeding the dynamic increase in cardiac efferent sympathetic nerve activity following myocardial ischemia.Basic Res Cardiol. 2016 May;111(3):35. doi: 10.1007/s00395-016-0556-3. Epub 2016 Apr 19. Basic Res Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27093872
-
Central administration of cocaine-amphetamine-regulated transcript activates hypothalamic neuroendocrine neurons in the rat.Endocrinology. 2000 Feb;141(2):794-801. doi: 10.1210/endo.141.2.7295. Endocrinology. 2000. PMID: 10650962
-
Acute sleep deprivation (ASD) and cardioprotection: Impact of ASD on oxytocin-mediated sympathetic nervous activation preceding myocardial infarction.Neuropeptides. 2024 Oct;107:102453. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2024.102453. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Neuropeptides. 2024. PMID: 38959559
-
A role for the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus in the autonomic control of heart and kidney.Exp Physiol. 2005 Mar;90(2):169-73. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2004.029041. Epub 2004 Dec 16. Exp Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15604110 Review.
Cited by
-
Vasopressin & Oxytocin in Control of the Cardiovascular System: An Updated Review.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2020;18(1):14-33. doi: 10.2174/1570159X17666190717150501. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31544693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Oxytocin in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease: Mechanisms and Signaling Pathways.Front Neurosci. 2019 May 21;13:454. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00454. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31178679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KLRD1, FOSL2 and LILRB3 as potential biomarkers for plaques progression in acute myocardial infarction and stable coronary artery disease.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021 Jul 16;21(1):344. doi: 10.1186/s12872-021-01997-5. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021. PMID: 34271875 Free PMC article.
-
Oxytocin: A Multi-Functional Biomolecule with Potential Actions in Dysfunctional Conditions; From Animal Studies and Beyond.Biomolecules. 2022 Oct 31;12(11):1603. doi: 10.3390/biom12111603. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36358953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impaired oxytocin signalling in the central amygdala in rats with chronic heart failure.J Physiol. 2024 Nov;602(22):6259-6280. doi: 10.1113/JP286297. Epub 2024 Nov 12. J Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39530490
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

