THR1 mediates GCN4 and CDC4 to link morphogenesis with nutrient sensing and the stress response in Candida albicans
- PMID: 30320368
- PMCID: PMC6202100
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3930
THR1 mediates GCN4 and CDC4 to link morphogenesis with nutrient sensing and the stress response in Candida albicans
Abstract
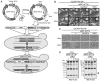
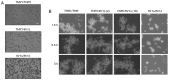
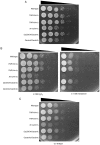
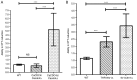
Candida albicans (C. albicans) CDC4 (CaCDC4), encoding the F‑box protein for the substrate specificity of the Skp1‑cullin‑F‑box E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, suppresses the yeast‑to‑filament transition in C. albicans. In our previous study, Thr1 was identified as a CaCdc4‑associated protein using affinity purification. THR1 encodes a homoserine kinase, which is involved in the threonine biosynthesis pathway. The present study generated a strain with repressible CaCDC4 expression and continuous THR1 expression. Colony and cell morphology analyses, as well as immunoblotting, revealed that the Thr1 protein was detectable under conditions in which the expression of CaCDC4 was repressed and that the filaments resulting from the repressed expression of CaCDC4 were suppressed by the constitutive expression of THR1 in C. albicans. Additionally, by using the CaSAT1‑flipper method, the present study produced null mutants of THR1, GCN4, and CaCDC4. The phenotypic consequences were evaluated by growth curves, spotting assays, microscopic analysis, reverse transcription‑polymerase chain reaction and XTT‑based biofilm formation ability. The results revealed that fewer cells lacking THR1 entered the stationary phase but had no apparent morphological alteration. It was observed that the expression of THR1 was upregulated concurrently with GCN4 during nutrient depletion and that cells lacking GCN4 rescued the lethality of cells in the absence of THR1 in conditions accumulating homoserine in the threonine biosynthesis pathway. Of note, it was found that cells with either CaCDC4 or THR1 loss were sensitive to oxidative stress and osmotic stress, with those with THR1 loss being more sensitive. In addition, it was observed that cells with loss of either CaCDC4 or THR1 exhibited the ability to increase biofilm formation, with those lacking CaCDC4 exhibiting a greater extent of enhancement. It was concluded that CaCDC4 is important in the coordination of morphogenesis, nutrient sensing, and the stress response through THR1 in C. albicans.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dissection of the Candida albicans Cdc4 protein reveals the involvement of domains in morphogenesis and cell flocculation.J Biomed Sci. 2013 Dec 20;20(1):97. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-20-97. J Biomed Sci. 2013. PMID: 24359552 Free PMC article.
-
A role of Candida albicans CDC4 in the negative regulation of biofilm formation.Can J Microbiol. 2015 Apr;61(4):247-55. doi: 10.1139/cjm-2014-0526. Epub 2014 Dec 19. Can J Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25719926
-
Affinity purification of Candida albicans CaCdc4-associated proteins reveals the presence of novel proteins involved in morphogenesis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010 Apr 23;395(1):152-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.03.162. Epub 2010 Mar 31. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010. PMID: 20361932
-
The metabolic basis of Candida albicans morphogenesis and quorum sensing.Fungal Genet Biol. 2011 Aug;48(8):747-63. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2011.04.002. Epub 2011 Apr 12. Fungal Genet Biol. 2011. PMID: 21513811 Review.
-
N-acetylglucosamine kinase, Hxk1 is a multifaceted metabolic enzyme in model pathogenic yeast Candida albicans.Microbiol Res. 2022 Oct;263:127146. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2022.127146. Epub 2022 Jul 26. Microbiol Res. 2022. PMID: 35940108 Review.
Cited by
-
More Than Just Cleaning: Ubiquitin-Mediated Proteolysis in Fungal Pathogenesis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Nov 10;11:774613. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.774613. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34858882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular targets for antifungals in amino acid and protein biosynthetic pathways.Amino Acids. 2021 Jul;53(7):961-991. doi: 10.1007/s00726-021-03007-6. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Amino Acids. 2021. PMID: 34081205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stress Conditions Affect the Immunomodulatory Potential of Candida albicans Extracellular Vesicles and Their Impact on Cytokine Release by THP-1 Human Macrophages.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 6;24(24):17179. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417179. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139005 Free PMC article.
-
Non-albicans Candida Species: Immune Response, Evasion Mechanisms, and New Plant-Derived Alternative Therapies.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Dec 21;9(1):11. doi: 10.3390/jof9010011. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36675832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Characterization of Candida auris Isolates at a Major Tertiary Care Center in Lebanon.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jan 25;12:770635. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.770635. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35145489 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

