Assessment of Altered Cholesterol Homeostasis by Xenobiotics Using Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry
- PMID: 30320450
- PMCID: PMC6205911
- DOI: 10.1002/cptx.65
Assessment of Altered Cholesterol Homeostasis by Xenobiotics Using Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
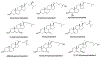
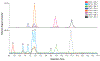
Cholesterol and cholesterol-derived oxysterols are critical for embryonic development, synapse formation and function, and myelination, among other biological functions. Indeed, alterations in levels of cholesterol, sterol precursors, and oxysterols result in a variety of developmental disorders, emphasizing the importance of cholesterol homeostasis. The ability of xenobiotics to reproduce similar phenotypes by altering cholesterol homeostasis has increasingly become of interest. Therefore, the ability to quantitatively assess alterations in cholesterol homeostasis resulting from exposure to xenobiotics is of value. This unit describes methods for the quantitative assessment of altered post-squalene cholesterol biosynthesis and subsequent oxysterol formation in various sample types using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS). Understanding alterations in cholesterol homeostasis resulting from xenobiotic exposure can provide key insight into the toxicant's mechanism of action and resulting phenotype. © 2018 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Keywords: cholesterol; homeostasis; liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry; oxysterols; sterols; xenobiotics.
© 2018 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- de Medina P, Paillasse MR, Segala G, Poirot M, Silvente-Poirot S, & Mangelsdorf DJ (2010). Identification and pharmacological characterization of cholesterol-5,6-epoxide hydrolase as a target for tamoxifen and AEBS ligands. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107(30), 13520–13525. National Academy of Sciences. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

