Global expression profiling of metabolic pathway-related lncRNAs in human gastric cancer and the identification of RP11-555H23.1 as a new diagnostic biomarker
- PMID: 30320481
- PMCID: PMC6818562
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.22692
Global expression profiling of metabolic pathway-related lncRNAs in human gastric cancer and the identification of RP11-555H23.1 as a new diagnostic biomarker
Abstract
Background: Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) have roles in regulating metabolism; however, the global expression profile of metabolic pathway-associated lncRNAs in gastric cancer is unknown. The purpose of our study was to examine metabolic pathway-related lncRNAs in gastric cancer and their possible diagnostic values.
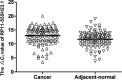
Methods: Differential expression patterns of metabolic pathway-related lncRNAs between gastric cancer and paired nontumor tissues were detected using metabolic pathway-associated lncRNA microarrays. The expression of RP11-555H23.1, one representative metabolic pathway-associated lncRNA, was validated using quantitative real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). The associations between RP11-55H23.1 expression and the clinicopathological features of gastric cancer patients were analyzed. A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was further established.
Results: A total of 114 differentially expressed metabolic pathway-associated lncRNAs (fold change >2, P < 0.05) between cancer and nontumor tissues were found (GEO No. GSE96856). Among them, TUG1, RP11-555H23.1, RP1-257I20.13, UGP2, GCSHP3, and XLOC_000889 lncRNAs were downregulated more than sixfold in gastric cancer tissues. In contrast, RP11-605F14.2, TBC1D3P5, BC130595, LINC00475, RP11-19P22.6, BC080653, XLOC_004923, AFAP1-AS1, EPB49, and RP11-296I10.3 lncRNAs were upregulated more than sixfold in gastric cancer tissues. We further demonstrated that RP11-555H23.1 expression was significantly correlated with TNM stage (P = 0.038). The area under the ROC curve (AUC) was 0.65, and the specificity and sensitivity were 62% and 81%, respectively.
Conclusions: Metabolic pathway-associated lncRNAs play an important role in the occurrence of gastric cancer, and metabolic pathway-associated lncRNAs, such as RP11-555H23.1, may represent novel biomarkers of gastric cancer.
Keywords: RP11-555H23.1; biomarker; gastric cancer; long noncoding RNA; metabolic pathway.
© 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- Chen S, Li T, Zhao Q, Xiao B, Guo J. Using circular RNA hsa_circ_0000190 as a new biomarker in the diagnosis of gastric cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 2017;466:167‐171. - PubMed
-
- Xie Y, Shao Y, Sun W, et al. Downregulated expression of hsa_circ_0074362 in gastric cancer and its potential diagnostic values. Biomark Med. 2018;12:11‐20. - PubMed
-
- Li T, Shao Y, Fu L, et al. Plasma circular RNA profiling of patients with gastric cancer and their droplet digital RT‐PCR detection. J Mol Med (Berl). 2018;96:85‐96. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

