An RXLR effector secreted by Phytophthora parasitica is a virulence factor and triggers cell death in various plants
- PMID: 30320960
- PMCID: PMC6637884
- DOI: 10.1111/mpp.12760
An RXLR effector secreted by Phytophthora parasitica is a virulence factor and triggers cell death in various plants
Abstract
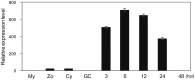
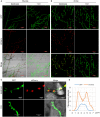
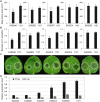
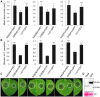
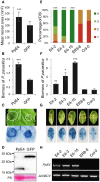
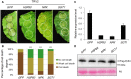
RXLR effectors encoded by Phytophthora species play a central role in pathogen-plant interactions. An understanding of the biological functions of RXLR effectors is conducive to the illumination of the pathogenic mechanisms and the development of disease control strategies. However, the virulence function of Phytophthora parasitica RXLR effectors is poorly understood. Here, we describe the identification of a P. parasitica RXLR effector gene, PPTG00121 (PpE4), which is highly transcribed during the early stages of infection. Live cell imaging of P. parasitica transformants expressing a full-length PpE4 (E4FL)-mCherry protein indicated that PpE4 is secreted and accumulates around haustoria during plant infection. Silencing of PpE4 in P. parasitica resulted in significantly reduced virulence on Nicotiana benthamiana. Transient expression of PpE4 in N. benthamiana in turn restored the pathogenicity of the PpE4-silenced lines. Furthermore, the expression of PpE4 in both N. benthamiana and Arabidopsis thaliana consistently enhanced plant susceptibility to P. parasitica. These results indicate that PpE4 contributes to pathogen infection. Finally, heterologous expression experiments showed that PpE4 triggers non-specific cell death in a variety of plants, including tobacco, tomato, potato and A. thaliana. Virus-induced gene silencing assays revealed that PpE4-induced cell death is dependent on HSP90, NPK and SGT1, suggesting that PpE4 is recognized by the plant immune system. In conclusion, PpE4 is an important virulence RXLR effector of P. parasitica and recognized by a wide range of host plants.
Keywords: Phytophthora parasitica; RXLR effector; cell death; haustoria; virulence.
© 2018 The Authors. Molecular Plant Pathology published by BSPP and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Short Linear Motifs (SLiMs) in "Core" RxLR Effectors of Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae: a Case of PpRxLR1 Effector.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Apr 27;10(2):e0177421. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01774-21. Epub 2022 Apr 11. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35404090 Free PMC article.
-
An RXLR effector PlAvh142 from Peronophythora litchii triggers plant cell death and contributes to virulence.Mol Plant Pathol. 2020 Mar;21(3):415-428. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12905. Epub 2020 Jan 7. Mol Plant Pathol. 2020. PMID: 31912634 Free PMC article.
-
The Cell Death Triggered by the Nuclear Localized RxLR Effector PITG_22798 from Phytophthora infestans Is Suppressed by the Effector AVR3b.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Feb 14;18(2):409. doi: 10.3390/ijms18020409. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28216607 Free PMC article.
-
Towards understanding the virulence functions of RXLR effectors of the oomycete plant pathogen Phytophthora infestans.J Exp Bot. 2009;60(4):1133-40. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ern353. Epub 2009 Feb 9. J Exp Bot. 2009. PMID: 19204033 Review.
-
Devastating intimacy: the cell biology of plant-Phytophthora interactions.New Phytol. 2020 Oct;228(2):445-458. doi: 10.1111/nph.16650. Epub 2020 Jun 19. New Phytol. 2020. PMID: 32394464 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Haustorium formation and a distinct biotrophic transcriptome characterize infection of Nicotiana benthamiana by the tree pathogen Phytophthora kernoviae.Mol Plant Pathol. 2021 Aug;22(8):954-968. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13072. Epub 2021 May 20. Mol Plant Pathol. 2021. PMID: 34018655 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of RXLR effectors from the New Zealand kauri dieback pathogen Phytophthora agathidicida.Mol Plant Pathol. 2020 Sep;21(9):1131-1148. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12967. Epub 2020 Jul 8. Mol Plant Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32638523 Free PMC article.
-
The Potato StNAC2-StSABP2 Module Enhanced Resistance to Phytophthora infestans Through Activating the Salicylic Acid Pathway.Mol Plant Pathol. 2025 May;26(5):e70081. doi: 10.1111/mpp.70081. Mol Plant Pathol. 2025. PMID: 40300849 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in PpAGO3 Lead to Enhanced Virulence of Phytophthora parasitica by Activation of 25-26 nt sRNA-Associated Effector Genes.Front Microbiol. 2022 Mar 24;13:856106. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.856106. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35401482 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the VQ Motif-Containing Protein Gene VQ28 Compromised Nonhost Resistance of Arabidopsis thaliana to Phytophthora Pathogens.Plants (Basel). 2022 Mar 24;11(7):858. doi: 10.3390/plants11070858. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35406838 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson, R.G. , Deb, D. , Fedkenheuer, K. and McDowell, J.M. (2015) Recent progress in RXLR effector research. Mol. Plant–Microbe Interact. 28, 1063–1072. - PubMed
-
- Attard, A. , Gourgues, M. , Callemeyn‐Torre, N. and Keller, H. (2010) The immediate activation of defense responses in Arabidopsis roots is not sufficient to prevent Phytophthora parasitica infection. New Phytol. 187, 449–460. - PubMed
-
- Bos, J.I. , Kanneganti, T.D. , Young, C. , Cakir, C. , Huitema, E. , Win, J. , Armstrong, M.R. , Birch, P.R. and Kamoun, S. (2006) The C‐terminal half of Phytophthora infestans RXLR effector AVR3a is sufficient to trigger R3a‐mediated hypersensitivity and suppress INF1‐induced cell death in Nicotiana benthamiana . Plant J. 48, 165–176. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

