A Reappraisal of Sex-Specific Cancer Survival Trends Among Adolescents and Young Adults in the United States
- PMID: 30321398
- PMCID: PMC6510224
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djy140
A Reappraisal of Sex-Specific Cancer Survival Trends Among Adolescents and Young Adults in the United States
Abstract
Background: Cancer survival among adolescents and young adults (AYAs) was previously reported as showing little or no improvement compared to younger or older counterparts. The role of the HIV/AIDS epidemic in the AYA survival deficit has not been evaluated.
Methods: Using cancer registry data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results program (SEER 9), we examined sex-specific 5-year relative survival trends for children (0-14 years old), AYAs (15-39 years old), and older adults (40 years and older) diagnosed with cancer during 1973-2009 and followed through the end of 2014. The analysis was conducted with and without Kaposi sarcoma (KS) and lymphomas, and by two time periods: 1973-1977 (before the human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome [HIV/AIDS] epidemic) and 2005-2009 (after the HIV/AIDS epidemic waned).
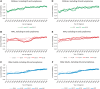
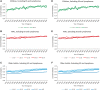
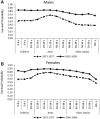
Results: A total of 3 209 721 invasive cancer cases were included in the study (27 646 children, 213 930 AYAs, and 2 968 145 older adults; 24 803 children, 178 741 AYAs, and 2 844 062 older adults when KS and lymphoma cases were excluded). We found that 5-year relative survival for AYAs exceeded that of children and older adults before the onset of the HIV/AIDS epidemic (eg, during 1973-1979, 0.58-0.67 among male AYAs as compared with 0.47-0.61 for male children and 0.36-0.42 for male older adults; among female AYAs, the numbers were 0.73-0.77 as compared with 0.51-0.65 for female children and 0.52-0.55 for female older adults); substantially declined during 1983-1997 when HIV/AIDS lacked effective treatment among male AYAs; and returned to be higher than most age groups by the late 1990s after HIV/AIDS was controlled. Nonetheless, comparison of survival improvement between 1973-1977 and 2005-2009 demonstrated less progress in AYAs than other age groups, which was due to AYAs' better baseline survival and larger survival gains among children and older adults in recent years.
Conclusions: Apart from the temporary impact of HIV/AIDS, survival among AYA cancer patients has shown sustained improvement and superiority relative to other age groups. However, these encouraging findings do not negate the distinctive challenges in cancer diagnosis, treatment, and survivorship faced by AYAs.
© The Author(s) 2018. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Comment in
-
RE: A Reappraisal of Sex-Specific Cancer Survival Trends Among Adolescents and Young Adults in the United States.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2019 Jun 1;111(6):633-634. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djz019. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2019. PMID: 30793191 No abstract available.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A.. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(1):7–30. - PubMed
-
- National Cancer Institute. Adolescents and Young Adults With Cancer https://www.cancer.gov/types/aya. Accessed April 12, 2018.
-
- Bleyer A, Barr R, Hayes-Lattin B, Thomas D, Ellis C, Anderson B; Biology and Clinical Trials Subgroups of the US National Cancer Institute Progress Review Group in Adolescent and Young Adult Oncology. The distinctive biology of cancer in adolescents and young adults. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8(4):288–298. - PubMed
-
- Bleyer A, Budd T, Montello M.. Adolescents and young adults with cancer. Cancer. 2006;107(7 suppl):1645–1655. - PubMed
-
- Adolescent and Young Adult Oncology Progress Review Group. Closing the Gap: Research and Care Imperatives for Adolescents and Young Adults With Cancer U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health National Cancer Institute, LIVESTRONG Young Adult Alliance; 2006. NIH Pub. No. 06-6067. https://www.cancer.gov/types/aya/research/ayao-august-2006.pdf. Accessed April 12, 2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

