Characterizing emotional overeating among patients with and without binge-eating disorder in primary care
- PMID: 30321775
- PMCID: PMC6268114
- DOI: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2018.09.003
Characterizing emotional overeating among patients with and without binge-eating disorder in primary care
Abstract
Objective: Emotional overeating and loss-of-control eating are associated with poorer weight-related and psychiatric outcomes, yet our understanding of the relationship between these variables is limited, particularly among individuals in primary care. This study examined the frequency of emotional overeating and relationship with loss-of-control eating among patients with and without binge-eating disorder (BED) seeking weight loss treatment in primary care.
Method: Participants were 131 adults (n = 105 female) with overweight/obesity seeking weight loss treatment in primary care. Participants completed the Eating Disorder Examination (semi-structured interview) and Yale Emotional Overeating Scale, which measures emotional overeating episodes. Height and weight were measured. Mean age and BMI were 47.60 years and 35.31 kg/m2, respectively. BED criteria were met by n = 35 (26.7%) participants.
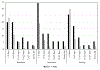
Results: Participants with BED endorsed more frequent emotional overeating episodes compared to those without BED. While total emotional overeating scores were not associated with loss-of-control eating, discrete types of emotional overeating episodes (e.g., loneliness) were associated with loss-of-control eating. Emotional overeating was most often reported in response to loneliness, boredom, or anxiety, which varied by BED status.
Conclusions: Most participants endorsed recent episodes of emotional overeating; those with BED endorsed more frequent episodes. Future research examining the impact of emotional overeating on weight loss treatment outcomes is warranted.
Keywords: Binge eating; Binge-eating disorder; Emotional eating; Obesity; Overweight; Primary care.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Emotional overeating and its associations with eating disorder psychopathology among overweight patients with binge eating disorder.Int J Eat Disord. 2006 Mar;39(2):141-6. doi: 10.1002/eat.20221. Int J Eat Disord. 2006. PMID: 16231349
-
Positive and negative emotional eating have different associations with overeating and binge eating: Construction and validation of the Positive-Negative Emotional Eating Scale.Appetite. 2017 Sep 1;116:423-430. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2017.05.035. Epub 2017 May 23. Appetite. 2017. PMID: 28549761
-
Eating pathology, emotion regulation, and emotional overeating in obese adults with Binge Eating Disorder.Eat Behav. 2013 Aug;14(3):309-13. doi: 10.1016/j.eatbeh.2013.05.008. Epub 2013 May 22. Eat Behav. 2013. PMID: 23910772 Free PMC article.
-
Emotional Eating, Binge Eating and Animal Models of Binge-Type Eating Disorders.Curr Obes Rep. 2017 Jun;6(2):217-228. doi: 10.1007/s13679-017-0265-8. Curr Obes Rep. 2017. PMID: 28434108 Review.
-
The Efficacy of Psychological Therapies in Reducing Weight and Binge Eating in People with Bulimia Nervosa and Binge Eating Disorder Who Are Overweight or Obese-A Critical Synthesis and Meta-Analyses.Nutrients. 2017 Mar 17;9(3):299. doi: 10.3390/nu9030299. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28304341 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Game Situation-Dependent Emotions on Sport Spectators' Food Craving.Front Psychol. 2021 Nov 18;12:724220. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.724220. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34867604 Free PMC article.
-
Consumed by Boredom: Food Choice Motivation and Weight Changes during the COVID-19 Pandemic.Behav Sci (Basel). 2022 Sep 28;12(10):366. doi: 10.3390/bs12100366. Behav Sci (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36285935 Free PMC article.
-
Eating Disorders and Intimate Partner Violence: The Influence of Fear of Loneliness and Social Withdrawal.Nutrients. 2022 Jun 24;14(13):2611. doi: 10.3390/nu14132611. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35807792 Free PMC article.
-
Emotional Eating Interventions for Adults Living With Overweight and Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Behaviour Change Techniques.J Hum Nutr Diet. 2025 Feb;38(1):e13410. doi: 10.1111/jhn.13410. J Hum Nutr Diet. 2025. PMID: 39763344 Free PMC article.
-
Two of a Kind? Mapping the Psychopathological Space between Obesity with and without Binge Eating Disorder.Nutrients. 2021 Oct 26;13(11):3813. doi: 10.3390/nu13113813. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34836069 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnow B, Kenardy J and Agras WS. The Emotional Eating Scale: the development of a measure to assess coping with negative affect by eating. Int J Eat Disord 1995;18:79–90. - PubMed
-
- Macht M How emotions affect eating: a five-way model. Appetite 2008;50:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Van Strien T, Rookus MA, Bergers GP, Frijters JE, Defares PB. Life events, emotional eating and change in body mass index. Int J Obes 1986;10:29–35. - PubMed
-
- Keller C and Siegrist M. Ambivalence toward palatable food and emotional eating predict weight fluctuations. Results of a longitudinal study with four waves. Appetite 2015;85:138–45. - PubMed
-
- Koenders PG and van Strien T. Emotional eating, rather than lifestyle behavior, drives weight gain in a prospective study in 1562 employees. J Occup Environ Med 2011;53:1287–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

