The Dual Role of TAM Receptors in Autoimmune Diseases and Cancer: An Overview
- PMID: 30322068
- PMCID: PMC6210017
- DOI: 10.3390/cells7100166
The Dual Role of TAM Receptors in Autoimmune Diseases and Cancer: An Overview
Abstract
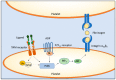
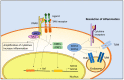
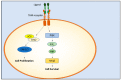
Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) regulate cellular processes by converting signals from the extracellular environment to the cytoplasm and nucleus. Tyro3, Axl, and Mer (TAM) receptors form an RTK family that plays an intricate role in tissue maintenance, phagocytosis, and inflammation as well as cell proliferation, survival, migration, and development. Defects in TAM signaling are associated with numerous autoimmune diseases and different types of cancers. Here, we review the structure of TAM receptors, their ligands, and their biological functions. We discuss the role of TAM receptors and soluble circulating TAM receptors in the autoimmune diseases systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and multiple sclerosis (MS). Lastly, we discuss the effect of TAM receptor deregulation in cancer and explore the therapeutic potential of TAM receptors in the treatment of diseases.
Keywords: Axl; Mer; TAM receptors; Tyro3; autoimmune disease; cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

