Executive Functioning Correlates With Communication Ability in Youth With Histories of Heavy Prenatal Alcohol Exposure
- PMID: 30322415
- PMCID: PMC6237635
- DOI: 10.1017/S1355617718000772
Executive Functioning Correlates With Communication Ability in Youth With Histories of Heavy Prenatal Alcohol Exposure
Abstract
Objectives: Caregivers of youth with heavy prenatal alcohol exposure report impaired communication, which can significantly impact quality of life. Using data collected as part of the Collaborative Initiative on Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (CIFASD), we examined whether cognitive variables predict communication ability of youth with histories of heavy prenatal alcohol exposure.
Methods: Subjects (ages 10-16 years) comprised two groups: adolescents with heavy prenatal alcohol exposure (AE) and non-exposed controls (CON). Selected measures of executive function (NEPSY, Delis-Kaplan Executive Function System), working memory (CANTAB), and language were tested in the child, while parents completed communication ratings (Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scales - Second Edition). Separate multiple regression analyses determined which cognitive domains predicted communication ability. A final, global model of communication comprised the three cognitive models.
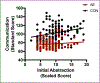
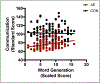
Results: Spatial Working Memory and Inhibition significantly contributed to communication ability across groups. Twenty Questions performance related to communication ability in the CON group only while Word Generation performance related to communication ability in the AE group only. Effects remained significant in the global model, with the exception of Spatial Working Memory.
Conclusions: Both groups displayed a relation between communication and Spatial Working Memory and Inhibition. Stronger communication ability related to stronger verbal fluency in the AE group and Twenty Questions performance in the CON group. These findings suggest that alcohol-exposed adolescents may rely more heavily on learned verbal storage or fluency for daily communication while non-exposed adolescents may rely more heavily on abstract thinking and verbal efficiency. Interventions aimed at aspects of executive function may be most effective at improving communication ability of these individuals. (JINS, 2018, 24, 1026-1037).
Keywords: Communication; Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASD); Fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS); Neurobehavioral disorder associated with prenatal alcohol exposure (ND-PAE); Neurobehavioral profile; Prenatal alcohol exposure.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Relation between adaptive function and IQ among youth with histories of heavy prenatal alcohol exposure.Birth Defects Res. 2019 Jul 15;111(12):812-821. doi: 10.1002/bdr2.1463. Epub 2019 Feb 4. Birth Defects Res. 2019. PMID: 30719847 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Executive function predicts adaptive behavior in children with histories of heavy prenatal alcohol exposure and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2012 Aug;36(8):1431-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2011.01718.x. Epub 2012 May 15. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2012. PMID: 22587709 Free PMC article.
-
Verbal and nonverbal fluency in children with heavy prenatal alcohol exposure.J Stud Alcohol. 2001 Mar;62(2):239-46. doi: 10.15288/jsa.2001.62.239. J Stud Alcohol. 2001. PMID: 11327190
-
[Formula: see text]Parent rating of executive function in fetal alcohol spectrum disorder: A review of the literature and new data on Aboriginal Canadian children.Child Neuropsychol. 2017 Aug;23(6):713-732. doi: 10.1080/09297049.2016.1191628. Epub 2016 Jun 10. Child Neuropsychol. 2017. PMID: 27282764 Review.
-
A meta-analytic review of adaptive functioning in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders, and the effect of IQ, executive functioning, and age.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2021 Dec;45(12):2430-2447. doi: 10.1111/acer.14728. Epub 2021 Nov 9. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2021. PMID: 34694016 Review.
Cited by
-
Executive and Social Functioning Across Development in Children and Adolescents With Prenatal Alcohol Exposure.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2021 Feb;45(2):457-469. doi: 10.1111/acer.14538. Epub 2021 Jan 22. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2021. PMID: 33349933 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Functional connectivity of the attention networks is altered and relates to neuropsychological outcomes in children with prenatal alcohol exposure.Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2021 Apr;48:100951. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2021.100951. Epub 2021 Apr 3. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33838597 Free PMC article.
-
Profiles of language and communication abilities in adolescents with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders.J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2023 Oct;29(8):724-733. doi: 10.1017/S1355617722000789. Epub 2022 Nov 3. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2023. PMID: 36325639 Free PMC article.
-
Oral and written communication skills of adolescents with prenatal alcohol exposure (PAE) compared with those with no/low PAE: A systematic review.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2021 Jul;56(4):694-718. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.12644. Epub 2021 Jun 16. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2021. PMID: 34137136 Free PMC article.
-
Neurodevelopmental Outcomes Associated with Prefrontal Cortical Deoxygenation in Children with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders.Dev Neuropsychol. 2020 Jan-Feb;45(1):1-16. doi: 10.1080/87565641.2020.1712604. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Dev Neuropsychol. 2020. PMID: 31914808 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akbarian GG (1992). Communication effects of prenatal alcohol exposure. Journal of Communication Disorders, 25, 221–240. - PubMed
-
- Burd L, Klug MG, Martsolf JT, & Kerbeshian J (2003). Fetal alcohol syndrome: neuropsychiatric phenomics. Neurotoxicology Teratology, 25, 697–705. - PubMed
-
- Cambridge Cognition Limited, CC (2006). Cantabeclipse version 3.0.0: Test administration guide. Cambridge Cognition Limited: Cambridge, UK.
-
- Carney LJ, & Chermak GD (1991). Performance of american indian children with fetal alcohol syndrome on the test of language development. Journal of Commuication Disorders, 24, 123–134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

