Fibrin-targeting immunotherapy protects against neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration
- PMID: 30323343
- PMCID: PMC6317891
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-018-0232-x
Fibrin-targeting immunotherapy protects against neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration
Abstract
Activation of innate immunity and deposition of blood-derived fibrin in the central nervous system (CNS) occur in autoimmune and neurodegenerative diseases, including multiple sclerosis (MS) and Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, the mechanisms that link disruption of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) to neurodegeneration are poorly understood, and exploration of fibrin as a therapeutic target has been limited by its beneficial clotting functions. Here we report the generation of monoclonal antibody 5B8, targeted against the cryptic fibrin epitope γ377-395, to selectively inhibit fibrin-induced inflammation and oxidative stress without interfering with clotting. 5B8 suppressed fibrin-induced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase activation and the expression of proinflammatory genes. In animal models of MS and AD, 5B8 entered the CNS and bound to parenchymal fibrin, and its therapeutic administration reduced the activation of innate immunity and neurodegeneration. Thus, fibrin-targeting immunotherapy inhibited autoimmunity- and amyloid-driven neurotoxicity and might have clinical benefit without globally suppressing innate immunity or interfering with coagulation in diverse neurological diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests
The authors declare competing financial interests.
Figures
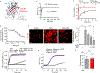
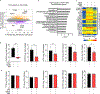
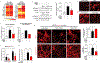
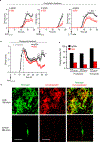
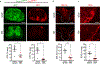
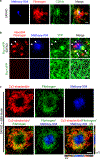
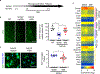
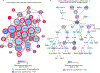
Comment in
-
Targeting fibrin in neurodegeneration.Nat Immunol. 2018 Nov;19(11):1149-1150. doi: 10.1038/s41590-018-0241-9. Epub 2018 Oct 15. Nat Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30323342 No abstract available.
References
-
- Rivest S Regulation of innate immune responses in the brain. Nat Rev Immunol 9, 429–439 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Lassmann H, van Horssen J & Mahad D Progressive multiple sclerosis: pathology and pathogenesis. Nat Rev Neurol 8, 647–656 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Heppner FL, Ransohoff RM & Becher B Immune attack: the role of inflammation in Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 16, 358–372 (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R21 NS108159/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 NS097976/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA082103/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 NS096920/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS052189/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS081149/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK090382/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007175/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- C06 RR018928/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS082976/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007334/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HD084387/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS092835/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K12 HD072222/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

