A facile consensus ranking approach enhances virtual screening robustness and identifies a cell-active DYRK1α inhibitor
- PMID: 30325204
- PMCID: PMC6479281
- DOI: 10.4155/fmc-2018-0198
A facile consensus ranking approach enhances virtual screening robustness and identifies a cell-active DYRK1α inhibitor
Abstract
Background: Virtual screening is vital for contemporary drug discovery but striking performance fluctuations are commonly encountered, thus hampering error-free use. Results and Methodology: A conceptual framework is suggested for combining screening algorithms characterized by orthogonality (docking-scoring calculations, 3D shape similarity, 2D fingerprint similarity) into a simple, efficient and expansible python-based consensus ranking scheme. An original experimental dataset is created for comparing individual screening methods versus the novel approach. Its utilization leads to identification and phosphoproteomic evaluation of a cell-active DYRK1α inhibitor.
Conclusion: Consensus ranking considerably stabilizes screening performance at reasonable computational cost, whereas individual screens are heavily dependent on calculation settings. Results indicate that the novel approach, currently available as a free online tool, is highly suitable for prospective screening by nonexperts.
Keywords: CREB1; NCI diversity set-II; NSC379099; analysis of residuals; docking-scoring calculations; fingerprint similarity; p53; phosphoproteomics; screening enrichment; shape-based similarity.
Conflict of interest statement
The screened compounds were provided free of charge from NCI/DTP repository (
No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures
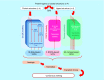
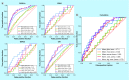
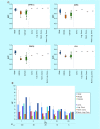



References
-
- Lagarde N, Zagury J-F, Montes M. Benchmarking data sets for the evaluation of virtual ligand screening methods: review and perspectives. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015;55(7):1297–1307. - PubMed
-
- Madhavi Sastry G, Adzhigirey M, Day T, Annabhimoju R, Sherman W. Protein and ligand preparation: parameters, protocols, and influence on virtual screening enrichments. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2013;27(3):221–234. - PubMed
-
• A very interesting and useful report on the impact of calculations setup on structure-based VS performance.
-
- Sheridan RP, Mcgaughey GB, Cornell WD. Multiple protein structures and multiple ligands: effects on the apparent goodness of virtual screening results. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2008;22(3):257–265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
