Evaluation of Serum Endocan Levels in Sensorineural Hearing Loss
- PMID: 30325334
- PMCID: PMC6483452
- DOI: 10.5152/iao.2018.5051
Evaluation of Serum Endocan Levels in Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study was to reveal the possible role of endothelial dysfunction in sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) by determining the serum endocan levels of patients with varying degrees of SNHL.
Materials and methods: Patients with documented SNHL and healthy controls were included in the study, whereas those with a known history of chronic inflammatory condition were excluded. In addition, a recent history of use of glucocorticoids, nonsteroid anti-inflammatory drugs, or any ototoxic medications was also considered as an exclusion criterion due to its potential impact on endocan synthesis and metabolism. Following overnight fasting, blood samples were collected, and serum endocan levels were measured. For statistical analysis of the data, PASW Statistics for Windows version 18 was used.
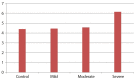
Results: The comparison of the subgroups yielded no statistically significant difference between the control and mild-to-moderate SNHL groups. Despite the increase in hearing loss, the difference between the endocan levels in these patients did not increase proportionately and was not statistically significant (p>0.05). The patients in the severe SNHL group had a higher level of serum endocan than those in other groups, and the difference was statistically significant (p<0.05).
Conclusion: The serum endocan levels failed to show a proportionate increase with increasing degree of SNHL, indicating that there is no precise association between SNHL and serum endocan levels. The serum endocan levels of patients with SNHL did not significantly differ from those of the healthy controls.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Correlation between endothelial dysfunction and sensorineural hearing loss].Vestn Otorinolaringol. 2025;90(3):13-18. doi: 10.17116/otorino20259003113. Vestn Otorinolaringol. 2025. PMID: 40530834 Russian.
-
Endocan: a novel predictor of endothelial dysfunction in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome.Clin Respir J. 2018 Jan;12(1):84-90. doi: 10.1111/crj.12487. Epub 2016 May 24. Clin Respir J. 2018. PMID: 27116287
-
Plasma levels of endothelial cell-specific molecule-1 and pentraxin-3 in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss.J Laryngol Otol. 2018 Nov;132(11):995-999. doi: 10.1017/S002221511800186X. Epub 2018 Oct 29. J Laryngol Otol. 2018. PMID: 30370871
-
Intratympanic dexamethasone for sudden sensorineural hearing loss after failure of systemic therapy.Laryngoscope. 2007 Jan;117(1):3-15. doi: 10.1097/01.mlg.0000245058.11866.15. Laryngoscope. 2007. PMID: 17202923 Review.
-
Endocan: A novel inflammatory indicator in cardiovascular disease?Atherosclerosis. 2015 Nov;243(1):339-43. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2015.09.030. Epub 2015 Sep 26. Atherosclerosis. 2015. PMID: 26448266 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources