Long-Term In Vitro Expansion of Epithelial Stem Cells Enabled by Pharmacological Inhibition of PAK1-ROCK-Myosin II and TGF-β Signaling
- PMID: 30332641
- PMCID: PMC6284236
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.09.072
Long-Term In Vitro Expansion of Epithelial Stem Cells Enabled by Pharmacological Inhibition of PAK1-ROCK-Myosin II and TGF-β Signaling
Abstract
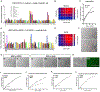
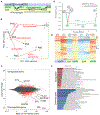
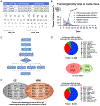
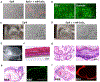
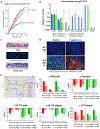
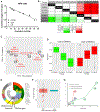
Despite substantial self-renewal capability in vivo, epithelial stem and progenitor cells located in various tissues expand for a few passages in vitro in feeder-free condition before they succumb to growth arrest. Here, we describe the EpiX method, which utilizes small molecules that inhibit PAK1-ROCK-Myosin II and TGF-β signaling to achieve over one trillion-fold expansion of human epithelial stem and progenitor cells from skin, airway, mammary, and prostate glands in the absence of feeder cells. Transcriptomic and epigenomic studies show that this condition helps epithelial cells to overcome stresses for continuous proliferation. EpiX-expanded basal epithelial cells differentiate into mature epithelial cells consistent with their tissue origins. Whole-genome sequencing reveals that the cells retain remarkable genome integrity after extensive in vitro expansion without acquiring tumorigenicity. EpiX technology provides a solution to exploit the potential of tissue-resident epithelial stem and progenitor cells for regenerative medicine.
Keywords: PAK1/ROCK/Myosin II; TGF-β; cell culture method; cell therapy; epithelial stem and progenitor cells; feeder-free; regenerative medicine.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Avior Y, Sagi I, and Benvenisty N (2016). Pluripotent stem cells in disease modelling and drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 17, 170–182. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

