Salt-Responsive Metabolite, β-Hydroxybutyrate, Attenuates Hypertension
- PMID: 30332647
- PMCID: PMC6542293
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.09.058
Salt-Responsive Metabolite, β-Hydroxybutyrate, Attenuates Hypertension
Abstract
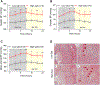
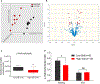
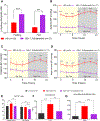
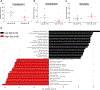
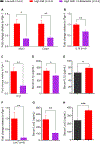
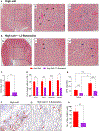
Dietary salt reduction and exercise are lifestyle modifications for salt-sensitive hypertensives. While exercise has prominent metabolic effects, salt has an adverse effect on metabolic syndrome, of which hypertension is a hallmark. We hypothesized that dietary salt impacts metabolism in a salt-sensitive model of hypertension. An untargeted metabolomic approach demonstrates lower circulating levels of the ketone body, beta-hydroxybutyrate (βOHB), in high salt-fed hypertensive rats. Despite the high salt intake, specific rescue of βOHB levels by nutritional supplementation of its precursor, 1,3-butanediol, attenuates hypertension and protects kidney function. This beneficial effect of βOHB was likely independent of gut-microbiotal and Th17-mediated effects of salt and instead facilitated by βOHB inhibiting the renal Nlrp3 inflammasome. The juxtaposed effects of dietary salt and exercise on salt-sensitive hypertension, which decrease and increase βOHB respectively, indicate that nutritional supplementation of a precursor of βOHB provides a similar benefit to salt-sensitive hypertension as exercise.
Keywords: Nlrp3; blood pressure; hypertension; inflammasome; inflammation; ketone body; kidney; metabolomics; salt; β-hydroxybutyrate.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
B.J. and S.C. have an interest in U.S. Patent Application serial no. 62/665,690 filed on May 2, 2018 in this paper regarding nutritional intervention for salt-sensitive hypertension for 1,3-butanediol. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Anders HJ, Suarez-Alvarez B, Grigorescu M, Foresto-Neto O, Steiger S, Desai J, Marschner JA, Honarpisheh M, Shi C, Jordan J, et al. (2018). The macrophage phenotype and inflammasome component NLRP3 contributes to nephrocalcinosis-related chronic kidney disease independent from IL-1-mediated tissue injury. Kidney Int. 93, 656–669. - PubMed
-
- Arima S, Uto H, Ibusuki R, Kumamoto R, Tanoue S, Mawatari S, Oda K, Numata M, Fujita H, Oketani M, et al. (2014). Hypertension exacerbates liver injury and hepatic fibrosis induced by a choline-deficient L-amino aciddefined diet in rats. Int. J. Mol. Med 33, 68–76. - PubMed
-
- Bai M, Chen Y, Zhao M, Zhang Y, He JC, Huang S, Jia Z, and Zhang A (2017). NLRP3 inflammasome activation contributes to aldosteroneinduced podocyte injury. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol 312, F556–F564. - PubMed
-
- Barbato JC, Koch LG, Darvish A, Cicila GT, Metting PJ, and Britton SL (1998). Spectrum of aerobic endurance running performance in eleven inbred strains of rats. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 85, 530–536. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

