Dietary Choline Intake: Current State of Knowledge Across the Life Cycle
- PMID: 30332744
- PMCID: PMC6213596
- DOI: 10.3390/nu10101513
Dietary Choline Intake: Current State of Knowledge Across the Life Cycle
Abstract
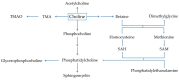
Choline, an essential dietary nutrient for humans, is required for the synthesis of the neurotransmitter, acetylcholine, the methyl group donor, betaine, and phospholipids; and therefore, choline is involved in a broad range of critical physiological functions across all stages of the life cycle. The current dietary recommendations for choline have been established as Adequate Intakes (AIs) for total choline; however, dietary choline is present in multiple different forms that are both water-soluble (e.g., free choline, phosphocholine, and glycerophosphocholine) and lipid-soluble (e.g., phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin). Interestingly, the different dietary choline forms consumed during infancy differ from those in adulthood. This can be explained by the primary food source, where the majority of choline present in human milk is in the water-soluble form, versus lipid-soluble forms for foods consumed later on. This review summarizes the current knowledge on dietary recommendations and assessment methods, and dietary choline intake from food sources across the life cycle.
Keywords: adequate intake; breast milk; choline; dietary assessment; dietary choline forms; dietary recommendations; human milk.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Patterson Y.K., Bhagwat A.S., Williams R.J., Howe C.J., Holden M.J. USD Database for The Choline Content of Common Foods, Release 2. Agricultural Research Service; Washington, DC, USA: 2008.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

