DYRK1A Protein, A Promising Therapeutic Target to Improve Cognitive Deficits in Down Syndrome
- PMID: 30332747
- PMCID: PMC6210095
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci8100187
DYRK1A Protein, A Promising Therapeutic Target to Improve Cognitive Deficits in Down Syndrome
Abstract
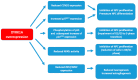
Down syndrome (DS) caused by a trisomy of chromosome 21 (HSA21), is the most common genetic developmental disorder, with an incidence of 1 in 800 live births. Its phenotypic characteristics include intellectual impairment, early onset of Alzheimer's disease, congenital heart disease, hypotonia, muscle weakness and several other developmental abnormalities, for the majority of which the pathogenetic mechanisms remain unknown. Among the numerous protein coding genes of HSA21, dual-specificity tyrosine-(Y)-phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A (DYRK1A) encodes a proline-directed serine/threonine and tyrosine kinase that plays pleiotropic roles in neurodevelopment in both physiological and pathological conditions. Numerous studies point to a crucial role of DYRK1A protein for brain defects in patients with DS. Thus, DYRK1A inhibition has shown benefits in several mouse models of DS, including improvement of cognitive behaviour. Lastly, a recent clinical trial has shown that epigallocatechine gallate (EGCG), a DYRK1A inhibitor, given to young patients with DS improved visual recognition memory, working memory performance and adaptive behaviour.
Keywords: DYRK1A; cognitive impairment; down syndrome; therapy; trisomy 21.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

