Effect of Consumption of Cocoa-Derived Products on Uric Acid Crystallization in Urine of Healthy Volunteers
- PMID: 30332783
- PMCID: PMC6213556
- DOI: 10.3390/nu10101516
Effect of Consumption of Cocoa-Derived Products on Uric Acid Crystallization in Urine of Healthy Volunteers
Abstract
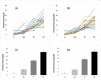
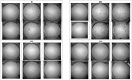
The purpose of this study was to determine the effects of consumption of different cocoa-derived products on uric acid crystallization in urine of 20 healthy volunteers. Participants were requested to select the specific diet that they wished to follow during the 12 h prior to collection of urine. The only restriction was that the diet could not include any product with cocoa, coffee, or caffeine. On the first day, each volunteer followed their selected diet, and an overnight 12 h urine sample was collected as the baseline urine. After seven days on an unrestricted diet, each volunteer repeated the same diet with 20 g of milk chocolate, chocolate powder, or dark chocolate during breakfast and another 20 g during dinner. Overnight 12 h urine samples were then collected. Urine volume, pH, oxalate, creatinine, uric acid, theobromine, and a uric acid crystallization test were determined for each sample. The results for all 20 patients show that uric acid crystallization was significantly lower following the consumption of chocolate powder or dark chocolate relative to baseline or following the consumption of milk chocolate. The results indicated that increased concentrations of urinary theobromine reduced the risk of uric acid crystallization.
Keywords: cocoa; theobromine; therapy; uric acid; urolithiasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of Two Dietary Supplements for Treatment of Uric Acid Renal Lithiasis: Citrate vs. Citrate + Theobromine.Nutrients. 2020 Jul 7;12(7):2012. doi: 10.3390/nu12072012. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32645831 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Methylxanthine composition and consumption patterns of cocoa and chocolate products.Prog Clin Biol Res. 1984;158:149-78. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1984. PMID: 6396642 Review.
-
Theobromine inhibits uric acid crystallization. A potential application in the treatment of uric acid nephrolithiasis.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 21;9(10):e111184. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111184. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25333633 Free PMC article.
-
Theobromine for treatment of uric acid stones and other diseases.Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2024 Nov 21;96(4):13277. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2024.13277. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2024. PMID: 39692405 Review.
-
HPLC method for urinary theobromine determination: Effect of consumption of cocoa products on theobromine urinary excretion in children.Clin Biochem. 2015 Nov;48(16-17):1138-43. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2015.06.022. Epub 2015 Jul 2. Clin Biochem. 2015. PMID: 26141736
Cited by
-
7-Methylxanthine Inhibits the Formation of Monosodium Urate Crystals by Increasing Its Solubility.Biomolecules. 2023 Dec 10;13(12):1769. doi: 10.3390/biom13121769. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 38136640 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Influence on Urolithiasis Risk Mediated by Plasma Metabolites: A Mendelian Randomization and Experimental Study Linking Genes, Metabolites, and Clinical Outcomes.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Aug 19;13(8):e70800. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70800. eCollection 2025 Aug. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40842671 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Cocoa Products Intake on Plasma and Urine Metabolites: A Review of Targeted and Non-Targeted Studies in Humans.Nutrients. 2019 May 24;11(5):1163. doi: 10.3390/nu11051163. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31137636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigations on melamine-based uric acid kidney stone formation and its prevention by inhibitors.Urolithiasis. 2023 Apr 11;51(1):68. doi: 10.1007/s00240-023-01437-3. Urolithiasis. 2023. PMID: 37039903
-
The power of desktop scanning electron microscopy with elemental analysis for analyzing urinary stones.Urolithiasis. 2023 Mar 15;51(1):50. doi: 10.1007/s00240-023-01424-8. Urolithiasis. 2023. PMID: 36920587 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ramello A., Vitale C., Marangella M. Epidemiology of nephrolithiasis. J. Nephrol. 2000;13:S65–S70. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

