Predictors of acute kidney injury in patients undergoing adult cardiac surgery
- PMID: 30333348
- PMCID: PMC6206792
- DOI: 10.4103/aca.ACA_21_18
Predictors of acute kidney injury in patients undergoing adult cardiac surgery
Abstract
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) after cardiac surgery (CS) is not uncommon and has serious effects on mortality and morbidity. A majority of patients suffer mild forms of AKI. There is a paucity of Indian data regarding this important complication after CS.
Aims and objectives: The primary objective was to study the incidence of AKI associated with CS in an Indian study population. Secondary objectives were to describe the risk factors associated with AKI-CS in our population and to generate outcome data in patients who suffer this complication.
Methods: Serial patients (n = 400) presenting for adult CS (emergency/elective) at a tertiary referral care hospital in South India from August 2016 to November 2017 were included as the study individuals. The incidence of AKI-CS AKI network (AKIN criteria), risk factors associated with this condition and the outcomes following AKI-CS are described.
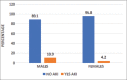
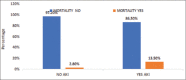
Results: Out of 400, 37 (9.25%) patients developed AKI after CS. AKI associated with CS was associated with a mortality of 13.5% (no AKI group mortality 2.8%, P = 0.001 [P < 0.05]). When AKI was severe enough to need renal replacement therapy, the mortality increased to 75%. Patients with AKI had a mean hospital stay 16.92 ± 12.75 days which was comparatively longer than patients without AKI (14 ± 7.98 days). Recent acute coronary syndrome, postoperative atrial fibrillation, and systemic hypertension significantly predicted the onset of AKI-CS in our population.
Conclusions: The overall incidence of AKI-CS was 9.25%. The incidence of AKI-CS requiring dialysis (Stage 3 AKIN) AKI-CS was lower (2%). However, mortality risks were disproportionately high in patients with AKIN Stage 3 AKI-CS (75%). There is a need for quality improvement in the care of patients with AKI-CS in its most severe forms since mortality risks posed by the development of Stage 3 AKIN AKI is higher than reported in other index populations from high resource settings.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; acute kidney injury network criteria; cardiac surgery; mortality; renal failure requiring dialysis; risk stratification.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest
Figures

References
-
- Hu J, Chen R, Liu S, Yu X, Zou J, Ding X. Global incidence and outcomes of adult patients with acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2016;30:82–9. - PubMed
-
- Kim MY, Jang HR, Huh W, Kim YG, Kim DJ, Lee YT, et al. Incidence, risk factors, and prediction of acute kidney injury after off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting. Ren Fail. 2011;33:316–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
