Starvation-induced Liver Enzyme Elevation after Initiation of Feeding
- PMID: 30333418
- PMCID: PMC6443550
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1663-18
Starvation-induced Liver Enzyme Elevation after Initiation of Feeding
Abstract
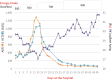
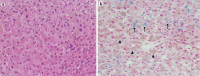
Exacerbation of liver enzymes after the initiation of feeding in malnourished patients is caused by refeeding syndrome or persistent starvation. There are no definite clinical markers for distinguishing between the two conditions. We herein report a 63-year-old woman with starvation-induced liver enzyme elevation. Her body weight was inversely associated with the liver enzyme levels after refeeding, which was a different course from refeeding syndrome. Normalization of liver enzymes ensued as the caloric intake increased and weight gain progressed. Daily changes in body weight can be a useful clinical marker for distinguishing between refeeding syndrome and starvation-induced liver enzyme elevation.
Keywords: body weight; liver enzyme; refeeding syndrome; resting energy expenditure; starvation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Solomon SM, Kirby DF. The refeeding syndrome: a review. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 14: 90-97, 1990. - PubMed
-
- Ozawa Y, Shimizu T, Shishiba Y. Elevation of serum aminotransferase as a sign of multiorgan-disorders in severely emaciated anorexia nervosa. Intern Med 37: 32-39, 1998. - PubMed
-
- Sakurai-Chin C, Ito N, Taguchi M, Miyakawa M, Takeshita A, Takeuchi Y. Hypoglycemic coma in a patient with anorexia nervosa coincident with acute exacerbation of liver injury induced by oral intake of nutrients. Intern Med 49: 1553-1556, 2010. - PubMed
-
- Narayanan V, Gaudiani JL, Harris RH, Mehler PS. Liver function test abnormalities in anorexia nervosa--cause or effect. Int J Eat Disord 43: 378-381, 2010. - PubMed

