DRUG-seq for miniaturized high-throughput transcriptome profiling in drug discovery
- PMID: 30333485
- PMCID: PMC6192987
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-06500-x
DRUG-seq for miniaturized high-throughput transcriptome profiling in drug discovery
Abstract
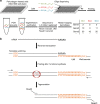
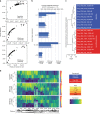
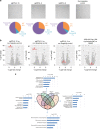
Here we report Digital RNA with pertUrbation of Genes (DRUG-seq), a high-throughput platform for drug discovery. Pharmaceutical discovery relies on high-throughput screening, yet current platforms have limited readouts. RNA-seq is a powerful tool to investigate drug effects using transcriptome changes as a proxy, yet standard library construction is costly. DRUG-seq captures transcriptional changes detected in standard RNA-seq at 1/100th the cost. In proof-of-concept experiments profiling 433 compounds across 8 doses, transcription profiles generated from DRUG-seq successfully grouped compounds into functional clusters by mechanism of actions (MoAs) based on their intended targets. Perturbation differences reflected in transcriptome changes were detected for compounds engaging the same target, demonstrating the value of using DRUG-seq for understanding on and off-target activities. We demonstrate DRUG-seq captures common mechanisms, as well as differences between compound treatment and CRISPR on the same target. DRUG-seq provides a powerful tool for comprehensive transcriptome readout in a high-throughput screening environment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

