Calcium/Calmodulin Kinase IV Controls the Function of Both T Cells and Kidney Resident Cells
- PMID: 30333818
- PMCID: PMC6176098
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02113
Calcium/Calmodulin Kinase IV Controls the Function of Both T Cells and Kidney Resident Cells
Abstract
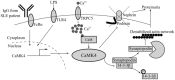
Calcium calmodulin kinase IV (CaMK4) regulates multiple processes that significantly contribute to the lupus-related pathology by controlling the production of IL-2 and IL-17 by T cells, the proliferation of mesangial cells, and the function and structure of podocytes. CaMK4 is also upregulated in podocytes from patients with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS). In both immune and non-immune podocytopathies, CaMK4 disrupts the structure and function of podocytes. In lupus-prone mice, targeted delivery of a CaMK4 inhibitor to CD4+ T cells suppresses both autoimmunity and the development of nephritis. Targeted delivery though to podocytes averts the deposition of immune complexes without affecting autoimmunity in lupus-prone mice and averts pathology induced by adriamycin in normal mice. Therefore, targeted delivery of a CaMK4 inhibitor to podocytes holds high therapeutic promise for both immune (lupus nephritis) and non-immune (FSGS) podocytopathies.
Keywords: CaMK4; IL-17; IL-2 deprivation; Treg deficiency; calcium/calmodulin kinase IV; podocyte dysfunction.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

