Genetic Association of Pulmonary Surfactant Protein Genes, SFTPA1, SFTPA2, SFTPB, SFTPC, and SFTPD With Cystic Fibrosis
- PMID: 30333828
- PMCID: PMC6175982
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02256
Genetic Association of Pulmonary Surfactant Protein Genes, SFTPA1, SFTPA2, SFTPB, SFTPC, and SFTPD With Cystic Fibrosis
Abstract
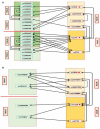
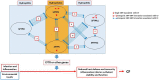
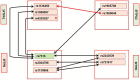
Surfactant proteins (SP) are involved in surfactant function and innate immunity in the human lung. Both lung function and innate immunity are altered in CF, and altered SP levels and genetic association are observed in Cystic Fibrosis (CF). We hypothesized that single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within the SP genes associate with CF or severity subgroups, either through single SNP or via SNP-SNP interactions between two SNPs of a given gene (intragenic) and/or between two genes (intergenic). We genotyped a total of 17 SP SNPs from 72 case-trio pedigree (SFTPA1 (5), SFTPA2 (4), SFTPB (4), SFTPC (2), and SFTPD (2)), and identified SP SNP associations by applying quantitative genetic principles. The results showed (a) Two SNPs, SFTPB rs7316 (p = 0.0083) and SFTPC rs1124 (p = 0.0154), each associated with CF. (b) Three intragenic SNP-SNP interactions, SFTPB (rs2077079, rs3024798), and SFTPA1 (rs1136451, rs1059057 and rs4253527), associated with CF. (c) A total of 34 intergenic SNP-SNP interactions among the 4 SP genes to be associated with CF. (d) No SNP-SNP interaction was observed between SFTPA1 or SFTPA2 and SFTPD. (e) Equal number of SNP-SNP interactions were observed between SFTPB and SFTPA1/SFTPA2 (n = 7) and SP-B and SFTPD (n = 7). (f) SFTPC exhibited significant SNP-SNP interactions with SFTPA1/SFTPA2 (n = 11), SFTPB (n = 4) and SFTPD (n = 3). (g) A single SFTPB SNP was associated with mild CF after Bonferroni correction, and several intergenic interactions that are associated (p < 0.01) with either mild or moderate/severe CF were observed. These collectively indicate that complex SNP-SNP interactions of the SP genes may contribute to the pulmonary disease in CF patients. We speculate that SPs may serve as modifiers for the varied progression of pulmonary disease in CF and/or its severity.
Keywords: SP-A; SP-B; SP-C; SP-D; cystic fibrosis; surfactant protein.
Figures
References
-
- Buscher R, Eilmes KJ, Grasemann H, Torres B, Knauer N, Sroka K, et al. beta2 adrenoceptor gene polymorphisms in cystic fibrosis lung disease. Pharmacogenetics (2002) 12:347–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

