Ligand Recognition Determines the Role of Inhibitory B Cell Co-receptors in the Regulation of B Cell Homeostasis and Autoimmunity
- PMID: 30333834
- PMCID: PMC6175988
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02276
Ligand Recognition Determines the Role of Inhibitory B Cell Co-receptors in the Regulation of B Cell Homeostasis and Autoimmunity
Abstract
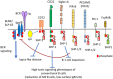
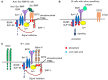
B cells express various inhibitory co-receptors including CD22, CD72, and Siglec-G. These receptors contain immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motifs (ITIMs) in the cytoplasmic region. Although many of the inhibitory co-receptors negatively regulate BCR signaling by activating SH2-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase 1 (SHP-1), different inhibitory co-receptors have distinct functional properties. CD22, Siglec-G, and CD72 preferentially regulate tonic signaling in conventional B cells, B-1 cell homeostasis, and development of lupus-like disease, respectively. CD72 recognizes RNA-related lupus self-antigen Sm/RNP as a ligand. This ligand recognition recruits CD72 to BCR in Sm/RNP-reactive B cells thereby suppressing production of anti-Sm/RNP autoantibody involved in the pathogenesis of lupus. In contrast, Siglec-G recognizes α2,3 as well as α2,6 sialic acids whereas CD22 recognizes α2,6 sialic acid alone. Because glycoproteins including BCR are dominantly glycosylated with α2,3 sialic acids in B-1 cells, Siglec-G but not CD22 recruits BCR as a ligand specifically in B-1 cells, and regulates B-1 cell homeostasis by suppressing BCR signaling in B-1 cells. Thus, recognition of distinct ligands determines functional properties of different inhibitory B cell co-receptors.
Keywords: B-1 cells; CD22; CD72; Sm/RNP; inhibitory B cell co-receptor; sialic acid; siglec-G; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

