Hepatocyte growth factor-induced mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor activation leads to insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor inhibitor unresponsiveness in gastric cancer cells
- PMID: 30333869
- PMCID: PMC6176415
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2018.9414
Hepatocyte growth factor-induced mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor activation leads to insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor inhibitor unresponsiveness in gastric cancer cells
Abstract
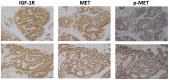
Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R) inhibitors have been developed as potential therapeutics for cancer treatment; however, the phase III trials have not produced promising overall survival rates. Therefore, understanding the mechanism underlying intrinsic resistance to IGF-1R-targeted agents is urgently required. A number of studies have revealed that activation of alternative receptor tyrosine kinases can mediate resistance to IGF-1R-targeted therapy. The present study investigated whether activated mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor (MET; also known as c-Met and hepatocyte growth factor receptor) confers resistance to an IGF-1R inhibitor (NVP-AEW541) of gastric cancer (GC) cells. NCI-N87 and MGC-803 cells were treated with varying concentrations and combinations of NVP-AEW541, hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and MET small interfering (si)-RNA or crizotinib (a MET inhibitor). The effects of these agents on cell proliferation and pro-apoptotic events were assessed by Cell Counting Kit-8 assays and flow cytometry. Receptor activation and the downstream signaling pathway were examined using western blot analysis. Expression and/or activation of MET and IGF-1R in 156 GC specimens were evaluated by immunohistochemistry. The results demonstrated that NVP-AEW541 inhibited cell growth, with dephosphorylation of IGF-1R and protein kinase B (AKT), in NCI-N87 and MGC-803 cells. Application of HGF activated MET and the downstream AKT signaling pathways, decreased apoptotic events and restored cell proliferation, which were reversed by MET inhibition via crizotinib or siRNA knockdown. Furthermore, combination therapy of NVP-AEW541 and crizotinib exhibited an enhanced effectiveness in vitro. In addition, >40% of IGF-1R overexpressed GC specimens showed MET expression and activation. In conclusion, HGF-induced MET activation may represent a novel mechanism conferring unresponsiveness to IGF-1R-targeted agents in GC, and inhibition of MET may improve the efficacy of IGF-1R inhibitors.
Keywords: drug resistance; gastric cancer; hepatocyte growth factor; insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor inhibitor; mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor.
Figures
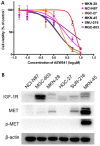
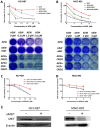
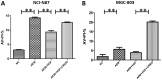

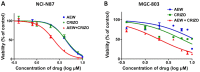
References
-
- Matsubara J, Yamada Y, Hirashima Y, Takahari D, Okita NT, Kato K, Hamaguchi T, Shirao K, Shimada Y, Shimoda T. Impact of insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor, epidermal growth factor receptor and HER2 expressions on outcomes of patients with gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:3022–3029. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1898. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Karp DD, Paz-Ares LG, Novello S, Haluska P, Garland L, Cardenal F, Blakely LJ, Eisenberg PD, Langer CJ, Blumenschein G, Jr, et al. Phase II study of the anti-insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor antibody CP-751,871 in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin in previously untreated, locally advanced, or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:2516–2522. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.19.9331. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
