Differential expression profiles of microRNAs in highly and weakly invasive/metastatic pancreatic cancer cells
- PMID: 30333874
- PMCID: PMC6176462
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2018.9352
Differential expression profiles of microRNAs in highly and weakly invasive/metastatic pancreatic cancer cells
Abstract
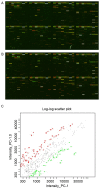
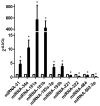
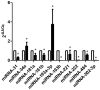
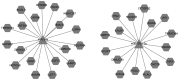
Pancreatic cancer is the eighth-leading cause of cancer-associated mortality worldwide. To date, the cellular and molecular mechanisms associated with the invasion and metastasis of pancreatic cancer remain unclear. To examine these mechanisms, a microRNA (miRNA/miR) microarray with 1,965 genes was hybridized with labeled miRNA probes from invasive PC-1.0 and non-invasive PC-1 cells for molecular profiling analysis. In addition, reverse transcription quantitative-polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) was utilized to validate the microarray results. Online miRNA target prediction algorithms online were used to predict the target genes of the differentially expressed miRNAs. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) term enrichment analysis were performed for the potential targets of the differentially expressed miRNAs. The results demonstrated that 54 miRNAs were differentially expressed, of which 33 were upregulated and 21 were downregulated in the PC-1.0 cell line compared with the PC-1 cell line. A total of 6 upregulated miRNAs (miR-31, -34a, -181a, -181b, -193a-3p, and -193b) and 4 downregulated miRNAs (miR-221, -222, -484, and -502-3p) were selected from these 54 miRNAs and validated by RT-qPCR. The differentially expressed miRNAs were further validated by RT-qPCR in the human pancreatic cancer cell lines AsPC-1 (highly invasive) and CAPAN-2 (less invasive). The results revealed that 2 upregulated miRNAs (miR-34a and -193a-3p) and 4 downregulated miRNAs (miR-221, -222, -484, and -502-3p) exhibited a consistent expression pattern between the PC-1.0/PC-1 and AsPC-1/CAPAN-2 pancreatic cancer cells. The GO and KEGG enrichment analysis indicated that the mRNAs potentially targeted by miRNAs were involved in a range of biological functions. These results suggest that different miRNA expression profiles occur between highly and weakly invasive and metastatic pancreatic cancer cell lines, and may affect a variety of biological functions in pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: invasion; metastasis; microRNA; microarray; pancreatic cancer.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Screening and identification of differentially expressed microRNAs in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma based on microRNA microarray.Oncol Lett. 2021 Nov;22(5):753. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.13014. Epub 2021 Aug 27. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 34539857 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration and validation of downregulated microRNA-199a-3p, downstream messenger RNA targets and transcriptional regulation in osteosarcoma.Am J Transl Res. 2019 Dec 15;11(12):7538-7554. eCollection 2019. Am J Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 31934299 Free PMC article.
-
Role of exosomal microRNA-125b-5p in conferring the metastatic phenotype among pancreatic cancer cells with different potential of metastasis.Life Sci. 2020 Aug 15;255:117857. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117857. Epub 2020 May 27. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32470446
-
Systematic enrichment analysis of microRNA expression profiling studies in endometriosis.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015 May;18(5):423-9. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26124927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAS in endometrial cancer: recent advances and potential clinical applications.EXCLI J. 2015 Feb 2;14:190-8. doi: 10.17179/excli2014-590. eCollection 2015. EXCLI J. 2015. PMID: 26535032 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-221 induces autophagy through suppressing HDAC6 expression and promoting apoptosis in pancreatic cancer.Oncol Lett. 2018 Dec;16(6):7295-7301. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9513. Epub 2018 Sep 27. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30546469 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-34 and gastrointestinal cancers: a player with big functions.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 May 9;24(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03338-w. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 38725047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterogeneous Types of miRNA-Disease Associations Stratified by Multi-Layer Network Embedding and Prediction.Biomedicines. 2021 Sep 3;9(9):1152. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9091152. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34572337 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Value and Correlation With Tumor Immune Infiltration of a Novel Metabolism-Related Gene Signature in Pancreatic Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Jan 19;11:757791. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.757791. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35127473 Free PMC article.
-
Role of MicroRNA-502-3p in Human Diseases.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Apr 2;16(4):532. doi: 10.3390/ph16040532. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37111289 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
