Long non-coding RNA, CHRF, predicts poor prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma and promotes cell proliferation and migration
- PMID: 30333887
- PMCID: PMC6176409
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2018.9425
Long non-coding RNA, CHRF, predicts poor prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma and promotes cell proliferation and migration
Abstract
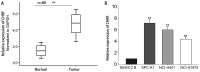
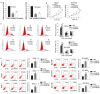
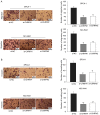
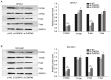
Research has demonstrated that long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are crucial factors in carcinogenesis. LncRNA, cardiac hypertrophy-related factor (CHRF), has been demonstrated to act as an oncogene in a variety of types of tumor. However, its biological function in lung adenocarcinoma remains to be elucidated. The present study aimed to examine the level of CHRF expression in lung adenocarcinoma tissues and cell lines, and to analyze the association between CHRF and clinicopathological characteristics, as well prognosis of patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Loss-of-function assays were performed to determine the biological function of CHRF. The expression of CHRF was markedly upregulated in lung adenocarcinoma tissues and cell lines. Patients exhibiting upregulated CHRF also demonstrated advanced Tumor-Node-Metastasis stage, lymph node metastasis and larger tumor size compared with those exhibiting downregulated CHRF. Results of Cox proportional hazards regression analysis suggested that highly-expressed CHRF may be regarded as an independent prognostic factor of prognosis. In addition, loss-of-function assays indicated that downregulation of CHRF suppressed cell proliferation, migration and invasion, and induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Western blotting revealed that the phosphoinositide-3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway activity is reduced in lung adenocarcinoma following the knockdown of CHRF. Together, these results indicate that lncRNA, CHRF, may serve a critical role in the development and progression of lung adenocarcinoma, and may act as a novel prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target in lung adenocarcinoma.
Keywords: cardiac hypertrophy-related factor; long non-coding RNA; lung adenocarcinoma; migration; proliferation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
IL-1β-Triggered Long Non-coding RNA CHRF Induces Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Modulating the microRNA-489/Myd88 Axis.J Cancer. 2022 May 16;13(8):2620-2630. doi: 10.7150/jca.63256. eCollection 2022. J Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35711847 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA CHRF facilitates cardiac hypertrophy through regulating Akt3 via miR-93.Cardiovasc Pathol. 2018 Jul-Aug;35:29-36. doi: 10.1016/j.carpath.2018.04.003. Epub 2018 Apr 11. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2018. PMID: 29747050
-
Long Non-Coding RNA LUCAT1 Promotes Proliferation and Invasion in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Through AKT/GSK-3β Signaling Pathway.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(3):891-904. doi: 10.1159/000491957. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30032137
-
The role of long non-coding RNA AFAP1-AS1 in human malignant tumors.Pathol Res Pract. 2018 Oct;214(10):1524-1531. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2018.08.014. Epub 2018 Aug 20. Pathol Res Pract. 2018. PMID: 30173945 Review.
-
Differential expression and clinical significance of long non-coding RNAs in the development and progression of lung adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2024 Jun 6;14:1411672. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1411672. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38912059 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Roles of lncRNAs in NF-κB-Mediated Macrophage Inflammation and Their Implications in the Pathogenesis of Human Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 25;25(5):2670. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052670. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38473915 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ogawa E, Takenaka K, Katakura H, Adachi M, Otake Y, Toda Y, Kotani H, Manabe T, Wada H, Tanaka F. Perimembrane Aurora-A expression is a significant prognostic factor in correlation with proliferative activity in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) Ann Surg Oncol. 2008;15:547–554. doi: 10.1245/s10434-007-9653-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
