Toxicity of Checkpoint Inhibition in Advanced RCC: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 30334015
- PMCID: PMC6179114
- DOI: 10.3233/KCA-170017
Toxicity of Checkpoint Inhibition in Advanced RCC: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: Checkpoint inhibitors (CPI) have now been established as standard agents in the management of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC). Given the unique toxicity profiles of CPIs, a detailed understanding of their incidence rate and characteristics is critical.
Objective: To perform a systematic review for the analysis of the incidence rate and characteristics of toxicities in mRCC patients treated with CPIs in published clinical trials.
Methods: A systematic search of EMBASE (Ovid) and MEDLINE (Ovid) was conducted as per PRISMA guidelines to identify prospective clinical trials of checkpoint inhibitors in mRCC. The search method involved querying for the terms renal cell carcinoma or kidney carcinoma with any of the following: programmed cell death 1, PD-1, programmed cell death ligand 1, PD-L1, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4, CTLA-4, immunotherapy, checkpoint inhibitor, anti-PD-1, or anti-PD-L1. Only prospective clinical trials were included.
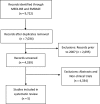
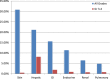
Results: The systematic review yielded 9,722 records through the MEDLINE (Ovid) and EMBASE (Ovid) databases. Ultimately, five prospective clinical trials with 722 patients were selected for inclusion. The rates of any grade adverse event (AE) and grade (G) 3-4 AEs were 79.9% and 20.9%, respectively. Regarding immune-related AEs (irAEs), the most common system affected by any grade irAE was the skin (30.89%) and the most common grade 3-4 irAE was related to the hepatic system (8.23%). Rates of AEs were similar across the CPI monotherapy clinical trials.
Conclusions: The rates of AEs in mRCC patients treated with CPI is similar to rates in other cancers. AEs in mRCC are fairly consistent among monotherapy trials with PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors and as one would expect higher when CTLA-4 and PD-1 inhibitors are offered in combination.
Keywords: CTLA-4; PD-1; PD-L1; Renal cell carcinoma; checkpoint inhibitors; immune-related adverse events; immunotherapy; kidney carcinoma; toxicity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Toxicity spectrum of immunotherapy in advanced lung cancer: A safety analysis from clinical trials and a pharmacovigilance system.EClinicalMedicine. 2022 Jul 1;50:101535. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101535. eCollection 2022 Aug. EClinicalMedicine. 2022. PMID: 35812997 Free PMC article.
-
The determinants of very severe immune-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A prospective study of the French REISAMIC registry.Eur J Cancer. 2021 Nov;158:217-224. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2021.08.048. Epub 2021 Oct 7. Eur J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34627664
-
Toxicity Profile of Combining PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors and Thoracic Radiotherapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 30;12:627197. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.627197. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33859637 Free PMC article.
-
Immune-related adverse events associated with programmed cell death protein-1 and programmed cell death ligand 1 inhibitors for non-small cell lung cancer: a PRISMA systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2019 Jun 10;19(1):558. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5701-6. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31182061 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in oncological and toxicity outcomes between programmed cell death-1 and programmed cell death ligand-1 inhibitors in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Treat Rev. 2021 Sep;99:102242. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2021.102242. Epub 2021 Jun 12. Cancer Treat Rev. 2021. PMID: 34153830
Cited by
-
Comments on "Deciphering RCC immunotherapy outcomes: insights from a Japanese multi-institutional study on the CANLPH score's impact".World J Urol. 2025 Mar 13;43(1):170. doi: 10.1007/s00345-025-05546-z. World J Urol. 2025. PMID: 40080156 No abstract available.
-
Acute Kidney Injury in Oncology Patients.J Cancer. 2020 May 22;11(16):4700-4708. doi: 10.7150/jca.45382. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32626516 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Immune Related Adverse Events and Outcome in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 18;13(4):860. doi: 10.3390/cancers13040860. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33670634 Free PMC article.
-
Adverse Events Associated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: Overview of Systematic Reviews.Drugs. 2022 May;82(7):793-809. doi: 10.1007/s40265-022-01707-1. Epub 2022 Apr 13. Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35416592 Review.
-
The Changing Therapeutic Landscape of Metastatic Renal Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Aug 22;11(9):1227. doi: 10.3390/cancers11091227. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31443471 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Peggs KS, Quezada SA, Korman AJ, Allison JP. Principles and use of anti-CTLA4 antibody in human cancer immunotherapy. Curr Opin Immunol 2006;18(2):206–13. - PubMed
-
- Herbst RS, Baas P, Kim DW, Felip E, Perez-Gracia JL, Han JY, et al. Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016;387(10027):1540–50. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials