Clinical response after laparoscopic fenestration of symptomatic hepatic cysts: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 30334152
- PMCID: PMC6394680
- DOI: 10.1007/s00464-018-6490-8
Clinical response after laparoscopic fenestration of symptomatic hepatic cysts: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Laparoscopic fenestration is one of the treatment options for symptomatic hepatic cysts, either solitary or in context of polycystic liver disease (PLD), but indications, efficacy and surgical techniques are under debate.
Methods: A systematic literature search (1950-2017) of PubMed, Embase, Web of Science and the Cochrane Library was performed (CRD42017071305). Studies assessing symptomatic relief or symptomatic recurrence after laparoscopic fenestration in patients with symptomatic, non-parasitic, hepatic cysts were included. Complications were scored according to Clavien-Dindo. Methodological quality was assessed by Newcastle-Ottawa scale (NOS) for cohort studies. Pooled estimates were calculated using a random effects model for meta-analysis.
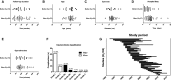
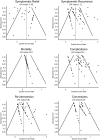
Results: Out of 5277 citations, 62 studies with a total of 1314 patients were included. Median NOS-score was 6 out of 9. Median follow-up duration was 30 months. Symptomatic relief after laparoscopic fenestration was 90.2% (95% CI 84.3-94.9). Symptomatic recurrence was 9.6% (95% CI 6.9-12.8) and reintervention rate was 7.1% (95% CI 5.0-9.4). Post-operative complications occurred in 10.8% (95% CI 8.1-13.9) and major complications in 3.3% (95% CI 2.1-4.7) of patients. Procedure-related mortality was 1.0% (95% CI 0.5-1.6). In a subgroup analysis of PLD patients (n = 146), symptomatic recurrence and reintervention rates were significantly higher with respective rates of 33.7% (95% CI 18.7-50.4) and 26.4% (95% CI 12.6-43.0). Complications were more frequent in PLD patients, with a rate of 29.3% (95% CI 16.0-44.5).
Conclusions: Laparoscopic fenestration is an effective procedure for treatment of symptomatic hepatic cysts with a low symptomatic recurrence rate. The symptomatic recurrence rate and risk of complications are significantly higher in PLD patients.
Keywords: Clinical outcomes; Hepatic cysts; Laparoscopic fenestration; Polycystic liver disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Drs. Lucas H.P. Bernts, Sebastiaan G. Echternach, Wietske Kievit, Camiel Rosman and Joost P.H. Drenth have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Laparoscopic management of symptomatic nonparasitic cysts of the liver. Indications and results.Ann Surg. 1994 Feb;219(2):157-64. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199402000-00007. Ann Surg. 1994. PMID: 8129486 Free PMC article.
-
[Laparoscopic treatment of non parasitic liver cysts].Ann Chir. 1996;50(6):419-25; discussion 426-30. Ann Chir. 1996. PMID: 8991197 French.
-
Laparoscopic cyst fenestration in the treatment of polycystic liver disease.Ann Ital Chir. 2014 May-Jun;85(3):298-303. Ann Ital Chir. 2014. PMID: 25073657
-
Laparoscopic fenestration vs open fenestration in patients with congenital hepatic cysts: a meta-analysis.World J Gastroenterol. 2011 Jul 28;17(28):3359-65. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i28.3359. World J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 21876626 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the Recurrence Rates of Nonparasitic Hepatic Cysts Treated With Laparoscopy or With Open Fenestration: A Meta-Analysis.Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2018 Apr;28(2):67-72. doi: 10.1097/SLE.0000000000000516. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2018. PMID: 29528948 Review.
Cited by
-
Prevalence of incidentally detected pancreatic cysts on magnetic resonance imaging in an adult population in Latin America.Radiol Bras. 2025 Apr 14;58:e20240103. doi: 10.1590/0100-3984.2024.0103. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Radiol Bras. 2025. PMID: 40264500 Free PMC article.
-
Laparoscopic complete excision of an enormous simple hepatic cyst occupying the entire abdomen in a child: a case report and literature review.Surg Case Rep. 2022 May 6;8(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s40792-022-01445-2. Surg Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35522346 Free PMC article.
-
Potential effect of tolvaptan on polycystic liver disease for patients with ADPKD meeting the Japanese criteria of tolvaptan use.PLoS One. 2022 Feb 17;17(2):e0264065. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0264065. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35176098 Free PMC article.
-
A new technique for the laparoscopic treatment of simple hepatic cysts.Surg Pract Sci. 2023 Apr 20;13:100171. doi: 10.1016/j.sipas.2023.100171. eCollection 2023 Jun. Surg Pract Sci. 2023. PMID: 39845400 Free PMC article.
-
Contemporary Management of Hepatic Cyst Disease: Techniques and Outcomes at a Tertiary Hepatobiliary Center.J Gastrointest Surg. 2021 Jan;25(1):77-84. doi: 10.1007/s11605-020-04821-1. Epub 2020 Oct 20. J Gastrointest Surg. 2021. PMID: 33083858 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

