RAGE in the pathophysiology of skeletal muscle
- PMID: 30334619
- PMCID: PMC6351676
- DOI: 10.1002/jcsm.12350
RAGE in the pathophysiology of skeletal muscle
Abstract
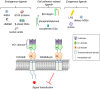
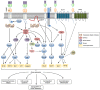
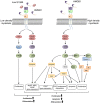
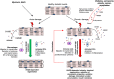
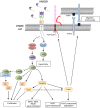
Emerging evidence suggests that the signalling of the Receptor for Advanced Glycation End products (RAGE) is critical for skeletal muscle physiology controlling both the activity of muscle precursors during skeletal muscle development and the correct time of muscle regeneration after acute injury. On the other hand, the aberrant re-expression/activity of RAGE in adult skeletal muscle is a hallmark of muscle wasting that occurs in response to ageing, genetic disorders, inflammatory conditions, cancer, and metabolic alterations. In this review, we discuss the mechanisms of action and the ligands of RAGE involved in myoblast differentiation, muscle regeneration, and muscle pathological conditions. We highlight potential therapeutic strategies for targeting RAGE to improve skeletal muscle function.
Keywords: AGEs; HMGB1; RAGE; S100B; muscle wasting; myogenesis.
© 2018 The Authors. Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of the Society on Sarcopenia, Cachexia and Wasting Disorders.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Advanced glycation end-products induce skeletal muscle atrophy and dysfunction in diabetic mice via a RAGE-mediated, AMPK-down-regulated, Akt pathway.J Pathol. 2016 Feb;238(3):470-82. doi: 10.1002/path.4674. Epub 2015 Dec 31. J Pathol. 2016. PMID: 26586640
-
S100b treatment overcomes RAGE signaling deficits in myoblasts on advanced glycation end-product cross-linked collagen and promotes myogenic differentiation.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024 Apr 1;326(4):C1080-C1093. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00502.2023. Epub 2024 Feb 5. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38314727
-
Molecular Characteristics of RAGE and Advances in Small-Molecule Inhibitors.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 27;22(13):6904. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136904. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34199060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Short-term pharmacologic RAGE inhibition differentially affects bone and skeletal muscle in middle-aged mice.Bone. 2019 Jul;124:89-102. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2019.04.012. Epub 2019 Apr 24. Bone. 2019. PMID: 31028960 Free PMC article.
-
RAGE Signaling in Melanoma Tumors.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 26;21(23):8989. doi: 10.3390/ijms21238989. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33256110 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Protective Effect of Brazilian Propolis against Glycation Stress in Mouse Skeletal Muscle.Foods. 2019 Sep 25;8(10):439. doi: 10.3390/foods8100439. Foods. 2019. PMID: 31557885 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Characterization of a Cancer Cachexia Rat Model Transplanted with Cells of the Rat Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell Line Sato Lung Cancer (SLC).Biomedicines. 2023 Oct 18;11(10):2824. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11102824. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37893197 Free PMC article.
-
Role of advanced glycation end products in the longitudinal association between muscular strength and psychotic symptoms among adolescents.Schizophrenia (Heidelb). 2022 Apr 27;8(1):44. doi: 10.1038/s41537-022-00249-5. Schizophrenia (Heidelb). 2022. PMID: 35853893 Free PMC article.
-
Reductive stress in striated muscle cells.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Sep;77(18):3547-3565. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03476-0. Epub 2020 Feb 18. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32072237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological Aspects of Selected Myokines in Skeletal Muscle: Focus on Aging.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 7;22(16):8520. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168520. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445222 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Frontera WR, Ochala J. Skeletal muscle: a brief review of structure and function. Calcif Tissue Int 2015;96:183–195. - PubMed
-
- Schiaffino S, Reggiani C. Fiber types in mammalian skeletal muscles. Physiol Rev 2011;91:1447–1531. - PubMed
-
- Neeper M, Schmidt AM, Brett J, Yan SD, Wang F, Pan YC, et al. Cloning and expression of a cell surface receptor for advanced glycosylation end products of proteins. J Biol Chem 1992;267:14998–15004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

