Clinical usefulness of 99mTc-HYNIC-TOC, 99mTc(V)-DMSA, and 99mTc-MIBI SPECT in the evaluation of pituitary adenomas
- PMID: 30334858
- PMCID: PMC6282662
- DOI: 10.1097/MNM.0000000000000931
Clinical usefulness of 99mTc-HYNIC-TOC, 99mTc(V)-DMSA, and 99mTc-MIBI SPECT in the evaluation of pituitary adenomas
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to evaluate the behavioral uptake and ability to diagnose pituitary adenoma (PA) using tumor-seeking radiopharmaceuticals, and to provide a semiquantitative analysis of tracer uptake in the pituitary region.
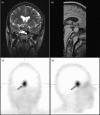
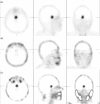
Patients and methods: The study included 33 (13 hormonally active and 20 nonfunctioning) patients with PA and 45 control participants without pituitary involvement. All patients (n=78) underwent single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) imaging with technetium-99m-labeled hydrazinonicotinyl-tyr-octreotide (Tc-HYNIC-TOC), dimercaptosuccinic acid (Tc(V)-DMSA) and hexakis-2-methoxyisobutylisonitrile (Tc-MIBI). A semiquantitative analysis of abnormal uptake was carried out by drawing identical regions of interest over the pituitary area and the normal brain on one transverse section that shows the lesion most clearly. The pituitary uptake to normal brain uptake (P/B) ratio was calculated in all cases.
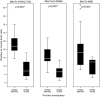
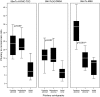
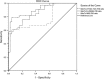
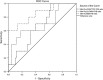
Results: The result of this study confirms that the SPECT semiquantitative method, with all three tracers, showed statistically significant differences between the PA group and the controls. However, Tc-HYNIC-TOC scintigraphy could have the highest diagnostic yield because of the smallest overlap between the P/B ratios between adenoma versus nonadenoma participants (the receiver operating characteristic curve P/B ratio cut-off value was 13.08). In addition, only Tc-MIBI SPECT have the diagnostic potential to detect secreting PAs, with statistically significant differences between groups (P<0.001), with an receiver operating characteristic curve P/B ratio cut-off value of 16.72.
Conclusion: A semiquantitative analysis of increased focal tracer uptake in the sellar area showed that Tc-HYNIC-TOC is a highly sensitive and reliable tumor-seeking agent for detecting PA, whereas Tc-MIBI SPECT is a highly sensitive and specific method in differentiating hormone-secreting pituitary tumor.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

