Neonatal giant hepatic hemangioma: A case report
- PMID: 30334996
- PMCID: PMC6211861
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012863
Neonatal giant hepatic hemangioma: A case report
Abstract
Rationale: Hepatic hemangioma is the third most common pediatric tumor, and it is rare in the neonatal period. This case study presents a rare case of hepatic hemangioma found in a neonate.
Patient concerns: A girl who was 18 days of age with the emergence of jaundice and an abdominal mass was admitted for physical examination in the local department.
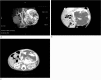
Diagnoses: An ultrasound showed that the hepatic left lobe was about 9 cm × 7 cm × 7 cm in size. A CT scan indicated a giant hemangioma in the hepatic left lobe. MRI detected a lesion measuring about 92 mm × 71 mm × 68 mm.
Interventions: The patient was treated with propranolol 3.5 mg PO bid (body weight 3.8 kg) after 1 week of admission for 4 weeks, but the mass did not appear to regress. Surgery was then performed successfully.
Outcomes: The patient recovered well without recurrence beyond one year.
Lessons: Imaging strategies and prenatal diagnosis are vital for the diagnosis of infantile hepatic hemangioma. Propranolol is effective in both cutaneous and hepatic multifocal and diffuse hemangioma. Adequate treatment time is necessary to cure the disease. The role of propranolol in massive hepatic hemangioma remains uncertain and needs further investigation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Historical and Contemporary Management of Infantile Hepatic Hemangioma: A 30-year Single-center Experience.Ann Surg. 2022 Jan 1;275(1):e250-e255. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003881. Ann Surg. 2022. PMID: 33064395
-
Multiple cutaneous and hepatic infantile hemangiomas having a successful response to propranolol as monotherapy at neonatal period.G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2013 Oct;148(5):525-30. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2013. PMID: 24005146 Review.
-
Efficacy of infantile hepatic hemangioma with propranolol treatment: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Jan;98(4):e14078. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014078. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 30681565 Free PMC article.
-
Multifocal infantile hepatic hemangiomas--imaging strategy and response to treatment after propranolol and steroids including review of the literature.Eur J Pediatr. 2012 Jul;171(7):1023-8. doi: 10.1007/s00431-011-1671-7. Epub 2012 Jan 11. Eur J Pediatr. 2012. PMID: 22234480 Review.
-
Intrahepatic mass-forming cholangiocarcinoma growing in a giant hepatic hemangioma: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Jul;98(27):e16410. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016410. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31277198 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Successful interventional treatment of huge hepatic haemangioma in a neonate following failed medical approach.BMJ Case Rep. 2024 Apr 2;17(4):e258909. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2023-258909. BMJ Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38569730
-
Neonatal hepatic hemangioma with intestinal obstruction: A report of two cases.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Aug 25;102(34):e34607. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000034607. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37653734 Free PMC article.
-
A report of 12 cases of congenital hepatic hemangioma and literature review.Front Pediatr. 2025 Apr 28;13:1453019. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1453019. eCollection 2025. Front Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40356783 Free PMC article.
-
Congenital hepatic hemangioma: an unusual case report of pulmonary hypertension.BMC Pediatr. 2023 Jun 7;23(1):284. doi: 10.1186/s12887-023-04096-w. BMC Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37286954 Free PMC article.
-
Management of Neonatal Hepatic Hemangiomas: A Single-Center Experience Focused on Challenging Cases.J Clin Med. 2024 May 11;13(10):2839. doi: 10.3390/jcm13102839. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38792380 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rawal N, Yazigi N. Pediatric liver transplantation. Pediatr Clin North Am 2017;64:677–84. - PubMed
-
- van der Meijs BB, Merks JH, de Haan TR, et al. Neonatal hepatic haemangioendothelioma: treatment options and dilemmas. Pediatr Radiol 2009;39:277–81. - PubMed
-
- Christison-Lagay ER, Burrows PE, Alomari A, et al. Hepatic hemangiomas: subtype classification and development of a clinical practice algorithm and registry. J Pediatr Surg 2007;42:62–7. discussion 67-68. - PubMed
-
- Konrad D, Ellis G, Perlman K. Spontaneous regression of severe acquired infantile hypothyroidism associated with multiple liver hemangiomas. Pediatrics 2003;112(6 pt 1):1424–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

