Intima-media complex thickness and carotid atherosclerotic plaque formation in Lublin's population in the context of selected comorbidities
- PMID: 30335922
- PMCID: PMC6440505
- DOI: 10.15557/JoU.2018.0019
Intima-media complex thickness and carotid atherosclerotic plaque formation in Lublin's population in the context of selected comorbidities
Abstract
Introduction: Atherosclerosis (arteriosclerosis) is a chronic arterial disease of the arteries with chronic inflammatory. The pathology of atherosclerosis is complex, and the atherosclerotic process is multi-factorial, not fully understood. Risk factors of atherosclerotic lesions may include: lipid disorders, hypertension or diabetes. One of the diagnostic methods of discovering atherosclerosis covers the assessment of the intima-media complex thickness by Doppler ultrasonography.
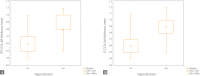
Aim: The aim of this report was an evaluation of the relationships between intima-media complex thickness in the right and left carotid arteries and the occurrence of atheromatous plaque in the Lublin population with respect to three possible concomitant medical conditions, mentioned above.
Material and methods: A group of 121 subjects was included into the study, all of the participants being residential inhabitants of the Lublin Voivodship. All the participating patients were requested to fill in a questionnaire. After that, the patients were submitted to Doppler sonography concentrated on intima-media complex thickness evaluation. The occurrence of atheromatous plaque was also assessed in obtained sonographic images.
Results: There were statistically significant differences for the intima-media complex thickness and for the atheromatous plaque according to all of the reported diseases: hypocholesterolaemia, hypertension and diabetes. Conclusions: The present study confirms that there is a relationship between the thickness of the intima-media complex in the right and left carotid arteries as well as the occurrence of the atherosclerotic plaque regarding the coexistence of specific disease entities in the subjects of the Lublin population.
Keywords: Doppler ultrasound; atherosclerotic plaque; carotid artery; carotid intima–media thickness; common.
© Polish Ultrasound Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Carotid intima-media thickness and plaque in borderline hypertension.Stroke. 1995 Jan;26(1):34-9. doi: 10.1161/01.str.26.1.34. Stroke. 1995. PMID: 7839394
-
[Risk factors of thickened intima-media and atherosclerotic plaque development in carotid arteries in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus].Ann Acad Med Stetin. 2008;54(2):22-32. Ann Acad Med Stetin. 2008. PMID: 19374227 Polish.
-
Atherosclerotic changes in the femoral and carotid arteries in familial hypercholesterolemia. Ultrasonographic assessment of intima-media thickness and plaque occurrence.Arterioscler Thromb. 1993 Oct;13(10):1404-11. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.13.10.1404. Arterioscler Thromb. 1993. PMID: 8399076
-
[Intima media thickness of the carotid arteries: early pointer to arteriosclerosis and therapeutic endpoint].Ultraschall Med. 2003 Jun;24(3):162-74. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-40058. Ultraschall Med. 2003. PMID: 12817310 Review. German.
-
[Carotid Ultrasound].Rinsho Byori. 2014 Sep;62(9):862-7. Rinsho Byori. 2014. PMID: 27526530 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Carotid imaging changes and serum IL-1β, sICAM-1, and sVAP-1 levels in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 9;10(1):21494. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78516-7. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33299063 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative/Antioxidative Status in Patients after Myocardial Infarction and in Those without Cardiovascular Event Depending on Anthropometric Factors Defining Body Weight.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Oct 23;16(21):4077. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16214077. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31652762 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma Campesterol Is Positively Associated with Carotid Plaques in Asymptomatic Subjects.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 9;23(19):11997. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911997. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233298 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Murray JL, Lopez AD: The Global Burden of Disease: A Comprehensive Assessment of Global Mortality and Disability from Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors in 1990 and Projected to 2020. World Health Organization, Geneva (Switzerland) 1996.
-
- Graham I, Atar D, Borch-Johnsen K, Boysen G, Burell G, Cifkova R. et al.: European guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice: full text. Fourth Joint Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and other societies on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice (constituted by representatives of nine societies and by invited experts). Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehab 2007; 14 (Suppl. 2): S1–S113. - PubMed
-
- Assmann G, Schulte H: Relation of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and triglycerides to incidence of atherosclerosis coronary artery disease (the PROCAM experience). Am J Cardiol 1992; 70: 733–737. - PubMed
-
- Nathan DM, Meigs J, Singer DE: The epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus: how sweet it is… or is it? Lancet 1997; 350 (Suppl. 1): S4–S9. - PubMed
-
- Duckworth W, Abraira C, Moritz T, Reda D, Emanuele N, Reaven PD. et al.: Glucose control and vascular complications in veterans with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2009; 360: 129–139. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources