Distinct cytokine profiles in human brains resilient to Alzheimer's pathology
- PMID: 30336198
- PMCID: PMC6437670
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nbd.2018.10.009
Distinct cytokine profiles in human brains resilient to Alzheimer's pathology
Abstract
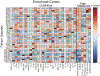
Our group has previously studied the brains of some unique individuals who are able to tolerate robust amounts of Alzheimer's pathological lesions (amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles) without experiencing dementia while alive. These rare resilient cases do not demonstrate the patterns of neuronal/synaptic loss that are normally found in the brains of typical demented Alzheimer's patients. Moreover, they exhibit decreased astrocyte and microglial activation markers GFAP and CD68, suggesting that a suppressed neuroinflammatory response may be implicated in human brain resilience to Alzheimer's pathology. In the present work, we used a multiplexed immunoassay to profile a panel of 27 cytokines in the brains of controls, typical demented Alzheimer's cases, and two groups of resilient cases, which possessed pathology consistent with either high probability (HP, Braak stage V-VI and CERAD 2-3) or intermediate probability (IP, Braak state III-IV and CERAD 1-3) of Alzheimer's disease in the absence of dementia. We used a multivariate partial least squares regression approach to study differences in cytokine expression between resilient cases and both Alzheimer's and control cases. Our analysis identified distinct profiles of cytokines in the entorhinal cortex (one of the earliest and most severely affected brain regions in Alzheimer's disease) that are up-regulated in both HP and IP resilient cases relative to Alzheimer's and control cases. These cytokines, including IL-1β, IL-6, IL-13, and IL-4 in HP resilient cases and IL-6, IL-10, and IP-10 in IP resilient cases, delineate differential inflammatory activity in brains resilient to Alzheimer's pathology compared to Alzheimer's cases. Of note, these cytokines all have been associated with pathogen clearance and/or the resolution of inflammation. Moreover, our analysis in the superior temporal sulcus (a multimodal association cortex that consistently accumulates Alzheimer's pathology at later stages of the disease along with overt symptoms of dementia) revealed increased expression of neurotrophic factors, such as PDGF-bb and basic FGF in resilient compared to AD cases. The same region also had reduced expression of chemokines associated with microglial recruitment, including MCP-1 in HP resilient cases and MIP-1α in IP resilient cases compared to AD. Altogether, our data suggest that different patterns of cytokine expression exist in the brains of resilient and Alzheimer's cases, link these differences to reduced glial activation, increased neuronal survival and preserved cognition in resilient cases, and reveal specific cytokine targets that may prove relevant to the identification of novel mechanisms of brain resiliency to Alzheimer's pathology.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Neuroinflammation; Partial least squares regression; Resilience.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations of interest: Dr. Gomez-Isla has participated as speaker in an Eli Lilly sponsored educational symposium and serves as member of an Eli Lilly Data Monitoring Committee (DMC). Dr. Lowe consults for Bayer Schering Pharma, Piramal Life Sciences and Merck Research and receives research support from GE Healthcare, Siemens Molecular Imaging, AVID Radiopharmaceuticals and the NIH (NIA, NCI). Dr. Morris has participated in Eli Lilly and Biogen sponsored trials.
Figures
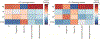



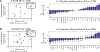
References
-
- Araujo DM, Cotman CW, 1992. Beta-amyloid stimulates glial cells in vitro to produce growth factors that accumulate in senile plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res 569, 141–5. - PubMed
-
- Araujo DM, Cotman CW, 1993. Trophic effects of interleukin-4, −7 and −8 on hippocampal neuronal cultures: potential involvement of glial-derived factors. Brain Res 600, 49–55. - PubMed
-
- Atreya R, et al., 2000. Blockade of interleukin 6 trans signaling suppresses T-cell resistance against apoptosis in chronic intestinal inflammation: evidence in crohn disease and experimental colitis in vivo. Nat Med 6, 583–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 GM008433/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062421/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG026276/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG007232/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG054023/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005134/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UF1 AG032438/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG037212/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001873/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG025204/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG006786/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG043511/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG016976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003991/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

