Integral dose based inverse optimization objective function promises lower toxicity in head-and-neck
- PMID: 30337013
- PMCID: PMC9608394
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2018.06.635
Integral dose based inverse optimization objective function promises lower toxicity in head-and-neck
Abstract
Purpose: The voxels in a CT data sets contain density information. Besides its use in dose calculation density has no other application in modern radiotherapy treatment planning. This work introduces the use of density information by integral dose minimization in radiotherapy treatment planning for head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC).
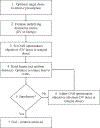
Materials and methods: Eighteen HNSCC cases were studied. For each case two intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) plans were created: one based on dose-volume (DV) optimization, and one based on integral dose minimization (Energy hereafter) inverse optimization. The target objective functions in both optimization schemes were specified in terms of minimum, maximum, and uniform doses, while the organs at risk (OAR) objectives were specified in terms of DV- and Energy-objectives respectively. Commonly used dosimetric measures were applied to assess the performance of Energy-based optimization. In addition, generalized equivalent uniform doses (gEUDs) were evaluated. Statistical analyses were performed to estimate the performance of this novel inverse optimization paradigm.
Results: Energy-based inverse optimization resulted in lower OAR doses for equivalent target doses and isodose coverage. The statistical tests showed dose reduction to the OARs with Energy-based optimization ranging from ∼2% to ∼15%.
Conclusions: Integral dose minimization based inverse optimization for HNSCC promises lower doses to nearby OARs. For comparable therapeutic effect the incorporation of density information into the optimization cost function allows reduction in the normal tissue doses and possibly in the risk and the severity of treatment related toxicities.
Keywords: Dose; IMRT; Imaging; Integral dose; Mass; Optimization.
Copyright © 2018 Associazione Italiana di Fisica Medica. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
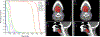
References
-
- Brizel DM, Vokes EE. Induction chemotherapy: to use or not to use? That is the question. Seminars in radiation oncology. 2009;19:11–6. - PubMed
-
- Bernier J. Current state-of-the-art for concurrent chemoradiation. Seminars in radiation oncology. 2009;19:3–10. - PubMed
-
- Browman GP, Hodson DI, Mackenzie RJ, Bestic N, Zuraw L. Choosing a concomitant chemotherapy and radiotherapy regimen for squamous cell head and neck cancer: A systematic review of the published literature with subgroup analysis. Head & neck. 2001;23:579–89. - PubMed
-
- El-Sayed S, Nelson N. Adjuvant and adjunctive chemotherapy in the management of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck region. A meta-analysis of prospective and randomized trials. J Clin Oncol. 1996;14:838–47. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

