Monotopic Membrane Proteins Join the Fold
- PMID: 30337134
- PMCID: PMC6309722
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2018.09.013
Monotopic Membrane Proteins Join the Fold
Abstract
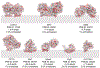
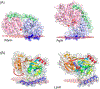
Monotopic membrane proteins, classified by topology, are proteins that embed into a single face of the membrane. These proteins are generally underrepresented in the Protein Data Bank (PDB), but the past decade of research has revealed new examples that allow the description of generalizable features. This Opinion article summarizes shared characteristics including oligomerization states, modes of membrane association, mechanisms of interaction with hydrophobic or amphiphilic substrates, and homology to soluble folds. We also discuss how associations of monotopic enzymes in pathways can be used to promote substrate specificity and product composition. These examples highlight the challenges in structure determination specific to this class of proteins, but also the promise of new understanding from future study of these proteins that reside at the interface.
Keywords: membrane interface; membrane–protein interaction; membranome; monotopic enzymes.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Forneris F and Mattevi A (2008) Enzymes without borders: mobilizing substrates, delivering products. Science 321 (5886), 213–6. - PubMed
-
- Krogh A et al. (2001) Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: application to complete genomes. J Mol Biol 305 (3), 567–80. - PubMed
-
- Krebs MP et al. (2004) Quality control of integral membrane proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 29 (12),648–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

