vWA proteins of Leptospira interrogans induce hemorrhage in leptospirosis by competitive inhibition of vWF/GPIb-mediated platelet aggregation
- PMID: 30337247
- PMCID: PMC6284457
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.10.033
vWA proteins of Leptospira interrogans induce hemorrhage in leptospirosis by competitive inhibition of vWF/GPIb-mediated platelet aggregation
Abstract
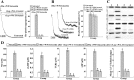
Backgroud: Leptospira interrogans is the major causative agent of leptospirosis, a worldwide zoonotic disease. Hemorrhage is a typical pathological feature of leptospirosis. Binding of von Willebrand factor (vWF) to platelet glycoprotein-Ibα (GPIbα) is a crucial step in initiation of platelet aggregation. The products of L. interrogans vwa-I and vwa-II genes contain vWF-A domains, but their ability to induce hemorrhage has not been determined.
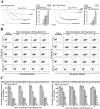
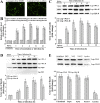
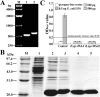
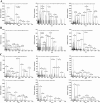
Methods: Human (Hu)-platelet- and Hu-GPIbα-binding abilities of the recombinant proteins expressed by L. interrogans strain Lai vwa-I and vwa-II genes (rLep-vWA-I and rLep-vWA-II) were detected by flowcytometry, surface plasmon resonance (SPR) and isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC). Hu-platelet aggregation and its signaling kinases and active components were detected by lumiaggregometry, Western analysis, spectrophotometry and confocal microscopy. Hu-GPIbα-binding sites in rLep-vWA-I and rLep-vWA-II were identified by SPR/ITC measurements.
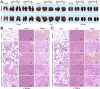
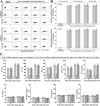
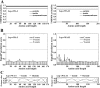
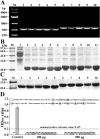
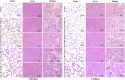
Findings: Both rLep-vWA-I and rLep-vWA-II were able to bind to Hu-platelets and inhibit rHu-vWF/ristocetin-induced Hu-platelet aggregation, but Hu-GPIbα-IgG, rLep-vWA-I-IgG and rLep-vWA-II-IgG blocked this binding or inhibition. SPR and ITC revealed a tight interaction between Hu-GPIbα and rLep-vWA-I/rLep-vWA-II with KD values of 3.87 × 10-7-8.65 × 10-8 M. Hu-GPIbα-binding of rL-vWA-I/rL-vWA-II neither activated the PI3K/AKT-ERK and PLC/PKC kinases nor affected the NO, cGMP, ADP, Ca2+ and TXA2 levels in Hu-platelets. G13/R36/G47 in Lep-vWA-I and G76/Q126 in Lep-vWA-II were confirmed as the Hu-GPIbα-binding sites. Injection of rLep-vWA-I or rLep-vWA-II in mice resulted in diffuse pulmonary and focal renal hemorrhage but this hemorrhage was blocked by rLep-vWA-I-IgG or rLep-vWA-II-IgG.
Interpretation: The products of L. interrogans vwa-I and vwa-II genes induce hemorrhage by competitive inhibition of vWF-mediated Hu-platelet aggregation.
Keywords: Competitive inhibition; Hemorrhage; Leptospira interrogans; Leptospirosis; Platelet aggregation; von Willebrand factor; vwa-I and vwa-II genes.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Leptospirosis is an invasive infectious and systemic inflammatory disease.Biomed J. 2020 Feb;43(1):24-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2019.12.002. Epub 2020 Feb 21. Biomed J. 2020. PMID: 32200953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of peptide antagonists to glycoprotein Ibalpha that selectively inhibit von Willebrand factor dependent platelet aggregation.Biochemistry. 2008 Apr 22;47(16):4674-82. doi: 10.1021/bi702428q. Epub 2008 Mar 26. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18363340
-
Identification of a novel 14-3-3zeta binding site within the cytoplasmic domain of platelet glycoprotein Ibalpha that plays a key role in regulating the von Willebrand factor binding function of glycoprotein Ib-IX.Circ Res. 2009 Dec 4;105(12):1177-85. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.204669. Epub 2009 Oct 29. Circ Res. 2009. PMID: 19875727
-
A novel Fas-binding outer membrane protein and lipopolysaccharide of Leptospira interrogans induce macrophage apoptosis through the Fas/FasL-caspase-8/-3 pathway.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2018 Jul 31;7(1):135. doi: 10.1038/s41426-018-0135-9. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2018. Retraction in: Emerg Microbes Infect. 2023 Dec;12(1):2240210. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2023.2240210. PMID: 30061622 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Platelet physiology and thrombosis.Thromb Res. 2004;114(5-6):447-53. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2004.07.020. Thromb Res. 2004. PMID: 15507277 Review.
Cited by
-
PD-L1 Regulates Platelet Activation and Thrombosis via Caspase-3/GSDME Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 15;13:921414. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.921414. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35784685 Free PMC article.
-
A Review on Host-Leptospira Interactions: What We Know and Future Expectations.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Nov 25;11:777709. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.777709. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34900757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leptospirosis is an invasive infectious and systemic inflammatory disease.Biomed J. 2020 Feb;43(1):24-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2019.12.002. Epub 2020 Feb 21. Biomed J. 2020. PMID: 32200953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leptospira interrogans Bat proteins impair host hemostasis by fibrinogen cleavage and platelet aggregation inhibition.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2020 Apr;209(2):201-213. doi: 10.1007/s00430-020-00664-4. Epub 2020 Feb 20. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32078713
-
Phagocyte Escape of Leptospira: The Role of TLRs and NLRs.Front Immunol. 2020 Oct 6;11:571816. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.571816. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33123147 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bharti A.R., Nally J.E., Ricaldi J.N. Leptospirosis: a zoonotic disease of global importance. Lancet Infect Dis. 2003;3(12):757–771. - PubMed
-
- Zhang C.L., Wang H., Yan J. Leptospirosis prevalence in Chinese populations in the last two decades. Microbes Infect. 2012;14(4):317–323. - PubMed
-
- Miraglia F., Matsuo M., Morais Z.M. Molecular characterization, serotyping, and antibiotic susceptibility profile of Leptospira interrogans serovar Copenhageni isolates from Brazil. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013;77(3):195–199. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

