miR-27a-3p protects against blood-brain barrier disruption and brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage by targeting endothelial aquaporin-11
- PMID: 30337368
- PMCID: PMC6311503
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.001858
miR-27a-3p protects against blood-brain barrier disruption and brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage by targeting endothelial aquaporin-11
Abstract
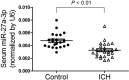
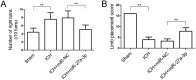
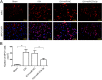
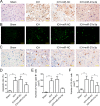
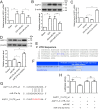
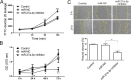
Previous studies have reported that miR-27a-3p is down-regulated in the serum of patients with intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), but the implication of miR-27a-3p down-regulation in post-ICH complications remains elusive. Here we verified miR-27a-3p levels in the serum of ICH patients by real-time PCR and observed that miR-27a-3p is also significantly reduced in the serum of these patients. We then further investigated the effect of miR-27a-3p on post-ICH complications by intraventricular administration of a miR-27a-3p mimic in rats with collagenase-induced ICH. We found that the hemorrhage markedly reduced miR-27a-3p levels in the hematoma, perihematomal tissue, and serum and that intracerebroventricular administration of the miR-27a-3p mimic alleviated behavioral deficits 24 h after ICH. Moreover, ICH-induced brain edema, vascular leakage, and leukocyte infiltration were also attenuated by this mimic. Of note, miR-27a-3p mimic treatment also inhibited neuronal apoptosis and microglia activation in the perihematomal zone. We further observed that the miR-27a-3p mimic suppressed the up-regulation of aquaporin-11 (AQP11) in the perihematomal area and in rat brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMECs). Moreover, miR-27a-3p down-regulation increased BMEC monolayer permeability and impaired BMEC proliferation and migration. In conclusion, miR-27a-3p down-regulation contributes to brain edema, blood-brain barrier disruption, neuron loss, and neurological deficits following ICH. We conclude that application of exogenous miR-27a-3p may protect against post-ICH complications by targeting AQP11 in the capillary endothelial cells of the brain.
Keywords: aquaporin; blood–brain barrier; brain; brain injury; endothelium; intracerebral hemorrhage; miR-27a-3p; microRNA (miRNA); neurological deficit; post-transcriptional regulation.
© 2018 Xi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures
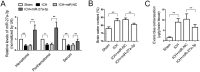
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-126-3p attenuates blood-brain barrier disruption, cerebral edema and neuronal injury following intracerebral hemorrhage by regulating PIK3R2 and Akt.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Dec 9;494(1-2):144-151. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.10.064. Epub 2017 Oct 14. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017. PMID: 29042193
-
Oxygen glucose deprivation-pretreated astrocyte-derived exosomes attenuates intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH)-induced BBB disruption through miR-27a-3p /ARHGAP25/Wnt/β-catenin axis.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2024 Jan 19;21(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s12987-024-00510-2. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2024. PMID: 38243347 Free PMC article.
-
miR-141-3p protects against blood-brain barrier disruption and brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage by targeting ZEB2.J Clin Neurosci. 2022 May;99:253-260. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2022.03.010. Epub 2022 Mar 17. J Clin Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35306455
-
Targeting Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response for Blood-Brain Barrier Protection in Intracerebral Hemorrhage.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022 Jul;37(1-3):115-134. doi: 10.1089/ars.2021.0072. Epub 2022 Jun 8. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022. PMID: 35383484 Review.
-
Dysregulation of microRNA and Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Roles in Neuroinflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 29;22(15):8115. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158115. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360881 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Non-coding RNAs in the regulation of blood-brain barrier functions in central nervous system disorders.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2022 Mar 26;19(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12987-022-00317-z. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2022. PMID: 35346266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs in central nervous system diseases: A prospective role in regulating blood-brain barrier integrity.Exp Neurol. 2020 Jan;323:113094. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2019.113094. Epub 2019 Oct 30. Exp Neurol. 2020. PMID: 31676317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coenzyme Q10 alleviates neurological deficits in a mouse model of intracerebral hemorrhage by reducing inflammation and apoptosis.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2025 Feb 28;250:10321. doi: 10.3389/ebm.2025.10321. eCollection 2025. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2025. PMID: 40093659 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review of MicroRNAs in Hemorrhagic Neurovascular Disease: Cerebral Cavernous Malformations as a Paradigm.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 17;26(8):3794. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083794. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332397 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-126-3p Attenuates Intracerebral Hemorrhage-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption by Regulating VCAM-1 Expression.Front Neurosci. 2019 Aug 16;13:866. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00866. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31474826 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

