Outcomes of Stent Retriever versus Aspiration-First Thrombectomy in Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 30337435
- PMCID: PMC7655372
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A5825
Outcomes of Stent Retriever versus Aspiration-First Thrombectomy in Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: There is ongoing debate regarding the optimal first-line thrombectomy technique for large-vessel occlusion.
Purpose: We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies on stent retriever-first and aspiration-first thrombectomy.
Data sources: We searched Ovid MEDLINE, PubMed, and EMBASE from 2009 to February 2018.
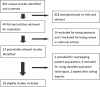
Study selection: Two reviewers independently selected the studies. The primary end point was successful reperfusion (TICI 2b/3).
Data analysis: Random-effects meta-analysis was used for analysis.
Data synthesis: Eighteen studies including 2893 patients were included. There was no significant difference in the rate of final successful reperfusion (83.9% versus 83.3%; OR = 0.87; 95% CI, 0.62%-1.27%) or good functional outcome (mRS 0-2) at 90 days (OR = 1.07; 95% CI, 0.80-1.44) between the stent-retriever thrombectomy and aspiration groups. The stent-retriever thrombectomy-first group achieved a statistically significant higher TICI 2b/3 rate after the first-line device than the aspiration-first group (74.9% versus 66.4%; OR = 1.53; 95% CI, 1.14%-2.05%) and resulted in lower use of a rescue device (19.9% versus 32.5%; OR = 0.36; 95% CI, 0.14%-0.90%). The aspiration-first approach resulted in a statistically shorter groin-to-reperfusion time (weighted mean difference, 7.15 minutes; 95% CI, 1.63-12.67 minutes). There was no difference in the number of passes, symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage, vessel dissection or perforation, and mortality between groups.
Limitations: Most of the included studies were nonrandomized. There was significant heterogeneity in some of the outcome variables.
Conclusions: Stent-retriever thrombectomy-first and aspiration-first thrombectomy were associated with comparable final reperfusion rates and functional outcome. Stent-retriever thrombectomy was superior in achieving reperfusion as a stand-alone first-line technique, with lower use of rescue devices but a longer groin-to-reperfusion time.
© 2018 by American Journal of Neuroradiology.
Figures


References
-
- Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. ; American Heart Association Stroke Council. 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2018;49:e46–110 10.1161/STR.0000000000000158 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
