Clinical Outcomes of Tuberculosis in Recipients After Living Donor Liver Transplantation
- PMID: 30337516
- PMCID: PMC6248277
- DOI: 10.12659/AOT.911034
Clinical Outcomes of Tuberculosis in Recipients After Living Donor Liver Transplantation
Abstract
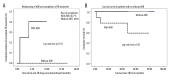
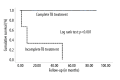
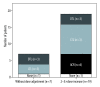
BACKGROUND This study aimed to determine clinical outcomes using various drugs during tuberculosis (TB) treatment among living donor liver transplant (LDLT) recipients with TB and to assess the impact of performing LDLT in patients with active TB at the time of LDLT. MATERIAL AND METHODS Out of 1313 LDLT performed from June 1994 to May 2016, 26 (2%) adult patients diagnosed with active TB were included in this study. Active TB was diagnosed using either TB culture, PCR, and/or tissue biopsy. RESULTS The median age was 56 years and the male/female ratio was 1.6: 1. Most patients had pulmonary TB (69.2%), followed by extrapulmonary and disseminated TB (15.4% each). Fourteen (53.8%) patients underwent LDLT even with the presence of active TB. All patients concurrently received anti-TB [Rifampicin-based: 13 (50%); Rifabutin-based: 12 (46.2%); INH-based: 1 (3.8%)] and immunosuppressive drugs [Tacrolimus-based: 6 (23%); Sirolimus/Everolimus-based: 20 (77%)]. During treatment, adverse drug reactions (ADR) occurred in 34.6% of patients: acute rejection in 6 (23.1%), hepatotoxicity in 2 (7.7%), and blurred vision in 1 (3.8%). Twenty-three (88%) patients completed their TB treatment. Neither TB recurrence nor TB-specific mortality were observed. Three (11.5%) patients died of non-TB-related causes. The overall 5-year survival rate was 86.2%. Patients with ADRs had a higher incidence of incomplete TB treatment (log-rank: p=0.012). Furthermore, patients with incomplete treatment were significantly associated with decreased overall survival (log-rank: p<0.001). Immunosuppressive and anti-TB drugs used during TB treatment and performing LDLT in patients with active TB at the time of LDLT were not associated with ADRs and overall survival. CONCLUSIONS Outcomes are generally favorable with intensive peri-operative evaluation and surveillance. ADRs and incomplete TB treatment may result in poor prognosis and increased mortality rates.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative analysis of the drug-drug interaction between immunosuppressants, safety and efficacy of rifabutin from rifampicin-based Anti-TB treatment in living donor liver transplant recipients with active tuberculosis.Biomed J. 2021 Dec;44(6 Suppl 2):S162-S170. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2020.08.010. Epub 2020 Sep 4. Biomed J. 2021. PMID: 35300949 Free PMC article.
-
Living-donor liver transplantation in patients with concurrent active tuberculosis at transplantation.Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2010 Aug;14(8):1039-44. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2010. PMID: 20626950
-
Tuberculosis in Egyptian kidney transplant recipients: study of clinical course and outcome.J Nephrol. 2003 May-Jun;16(3):404-11. J Nephrol. 2003. PMID: 12832742
-
Clinical presentation and outcome of tuberculosis in kidney, liver, and heart transplant recipients in Spain. Spanish Transplantation Infection Study Group, GESITRA.Transplantation. 1997 May 15;63(9):1278-86. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199705150-00015. Transplantation. 1997. PMID: 9158022 Review.
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in liver transplantation.Liver Transpl. 2010 Oct;16(10):1129-35. doi: 10.1002/lt.22133. Liver Transpl. 2010. PMID: 20879011 Review.
Cited by
-
Review article: latent tuberculosis in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases receiving immunosuppression-risks, screening, diagnosis and management.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Jul;56(1):6-27. doi: 10.1111/apt.16952. Epub 2022 May 20. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35596242 Free PMC article. Review.
-
"Access to pharmacy services is difficult in China": a qualitative study from the perspective of transplant recipients to explore their expectations.BMC Health Serv Res. 2024 Mar 27;24(1):387. doi: 10.1186/s12913-024-10733-6. BMC Health Serv Res. 2024. PMID: 38539184 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium Alginate Hydrogel Infusion of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and p38α Antagonistic Peptides in Myocardial Infarction Fibrosis Mitigation.J Am Heart Assoc. 2025 Apr 15;14(8):e036887. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.124.036887. Epub 2025 Apr 3. J Am Heart Assoc. 2025. PMID: 40178108 Free PMC article.
-
Tuberculosis in Pediatric Solid Organ and Hematopoietic Stem Cell Recipients.Glob Pediatr Health. 2021 Jan 15;8:2333794X20981548. doi: 10.1177/2333794X20981548. eCollection 2021. Glob Pediatr Health. 2021. PMID: 33506075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative analysis of the drug-drug interaction between immunosuppressants, safety and efficacy of rifabutin from rifampicin-based Anti-TB treatment in living donor liver transplant recipients with active tuberculosis.Biomed J. 2021 Dec;44(6 Suppl 2):S162-S170. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2020.08.010. Epub 2020 Sep 4. Biomed J. 2021. PMID: 35300949 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguado JM, Torre-Cisneros J, Fortun J, et al. Tuberculosis in solid-organ transplant recipients: consensus statement of the group for the study of infection in transplant recipients (GESITRA) of the Spanish Society of Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;48:1276–84. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control MoHaW, R.O.C. (Taiwan) 2016 Center for Disease Control Annual Report. Jun, 2016.
-
- Centers for Disease Control MoHaW, R.O.C. (Taiwan) Taiwan Tuberculosis Control Report 2013. Apr, 2014.
-
- Taiwan Ministry of Health and Welfare. 2015 Statistics cause of death. 2016. Sep 7,
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

